1. Introduction
Temperature is one of the most fundamental and widely measured physical parameters in industrial and daily life processes. Accurate temperature measurement and control are critical for ensuring product quality, improving production efficiency, conserving energy, and guaranteeing safety. Among all types of transmitters, temperature transmitters occupy a leading position in terms of quantity and application diversity.

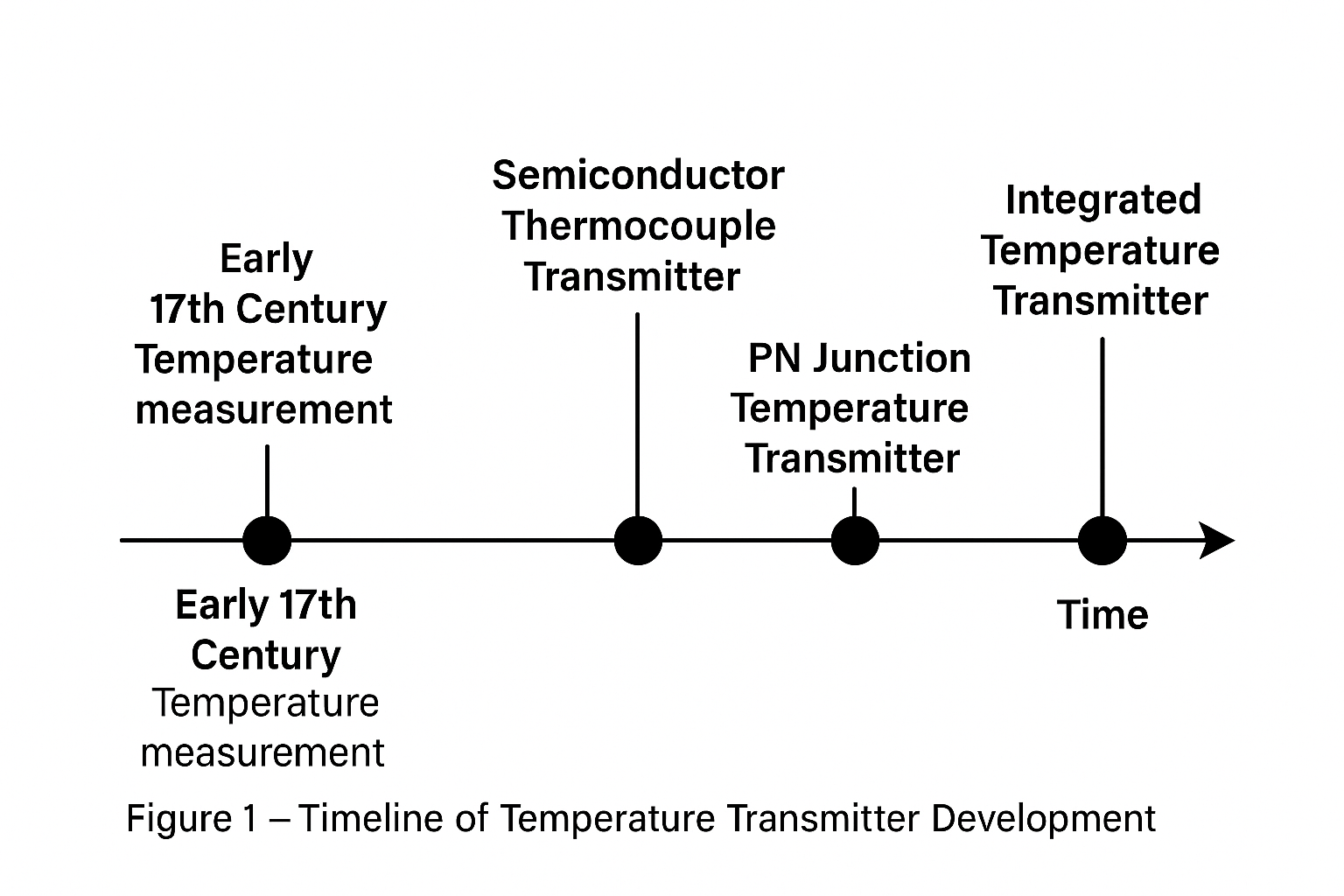
2. Historical Development
The concept of temperature measurement dates back to the early 17th century. With advancements in semiconductor technology, various types of temperature transmitters have been developed, including semiconductor thermocouple transmitters, resistance temperature transmitters, PN junction temperature transmitters, and integrated temperature transmitters.
3. Working Principle
Temperature transmitters operate by converting temperature changes into measurable electrical signals. Various materials and components exhibit property changes with temperature, which can be utilized for measurement:
Expansion (e.g., bimetallic strips)
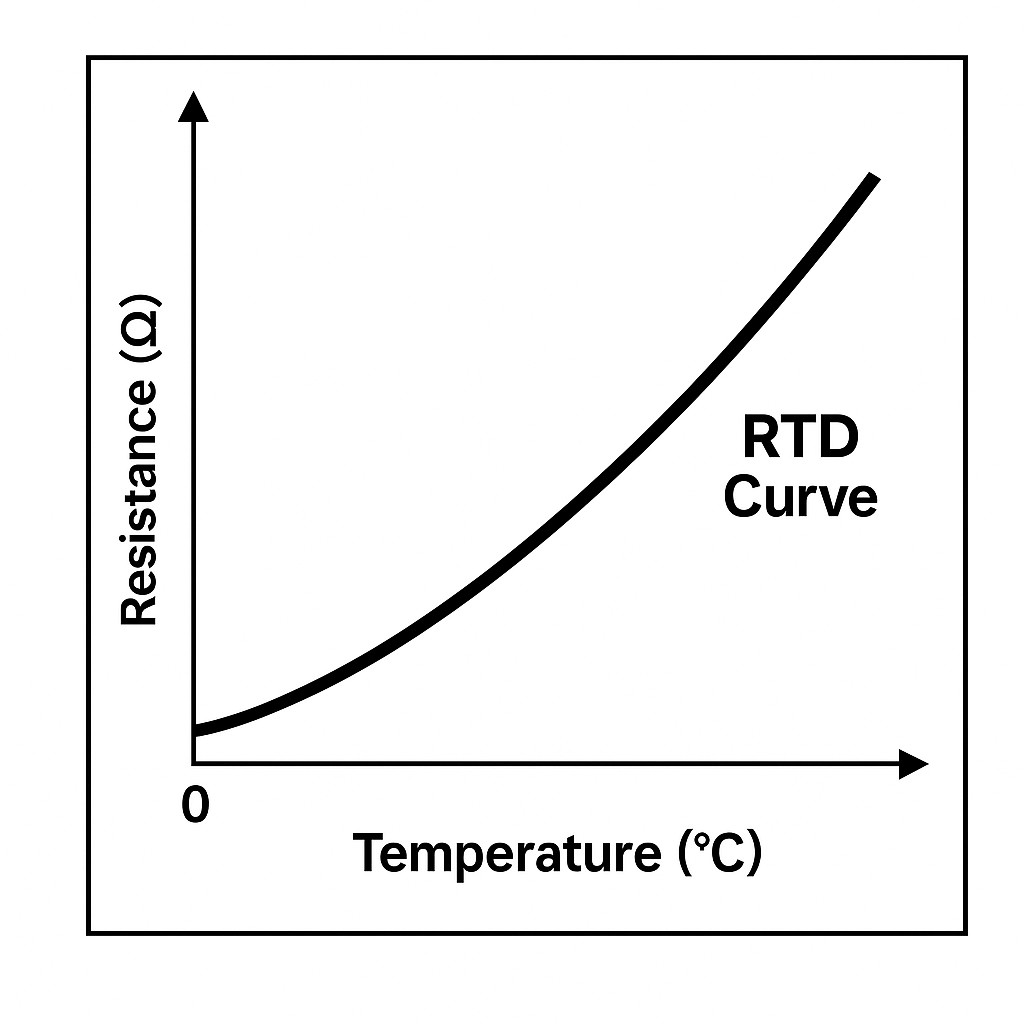
Resistance (e.g., RTDs, thermistors)
Capacitance
Electromotive force (e.g., thermocouples)
Magnetic properties
Frequency shifts
Optical characteristics
Thermal noise variations
4. Classification and Characteristics
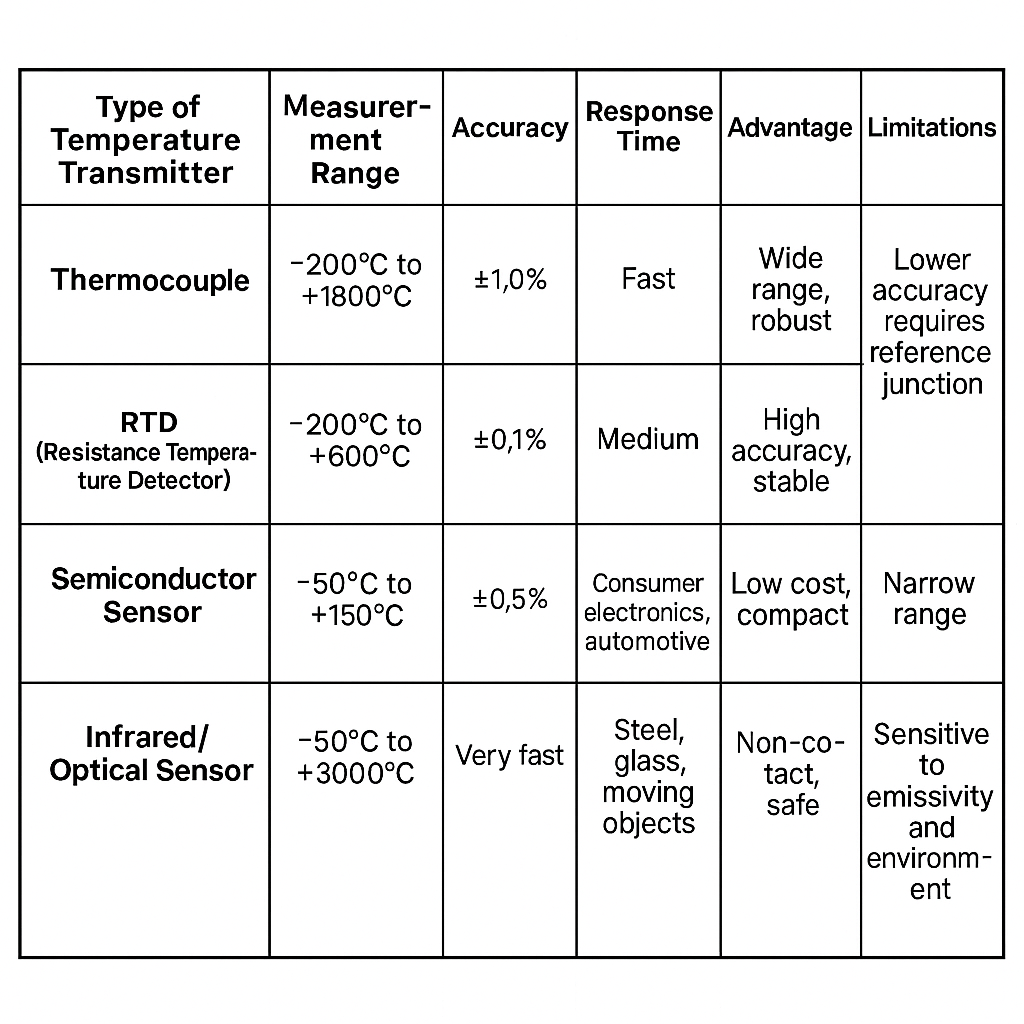
| Type of Temperature Transmitter | Measurement Range | Accuracy | Response Time | Typical Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple | -200°C to +1800°C | ±1.0% | Fast | Metallurgy, glass, ceramics | Wide range, robust | Lower accuracy, requires reference junction |
| RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) | -200°C to +600°C | ±0.1% | Medium | Chemical, power plants, HVAC | High accuracy, stable | Limited high-temp range |
| Semiconductor Sensor | -50°C to +150°C | ±0.5% | Fast | Consumer electronics, automotive | Low cost, compact | Narrow range |
| Infrared/Optical Sensor | -50°C to +3000°C | ±0.5% | Very fast | Steel, glass, moving objects | Non-contact, safe | Sensitive to emissivity and environment |
5. Application Areas
5.1 Industrial Production
Process industries: Monitoring reactors, boilers, turbines, and pipelines.
Energy conservation: Temperature control in furnaces and heat exchangers to reduce energy waste.
Safety assurance: Preventing overheating in chemical plants or power generation units.
5.2 Consumer Electronics and Household Appliances
Air conditioners, refrigerators, and water heaters utilize temperature transmitters for intelligent control and energy efficiency.
Mobile devices and computers use temperature monitoring to prevent overheating of CPUs and batteries.
5.3 Automotive and Transportation
Engine cooling systems, exhaust gas monitoring, and cabin climate control systems all rely on accurate temperature measurement.
5.4 Emerging Applications
Environmental monitoring: Ultraviolet and infrared detection.
Smart manufacturing: Integration with IoT and wireless communication.
Medical devices: Patient temperature monitoring and diagnostic equipment.
6. Market Trends and Future Outlook
With the rapid growth of industrial modernization and the expansion of the electronics and automotive sectors, the demand for temperature transmitters in China and worldwide has risen significantly.
Future developments will focus on:
Digitalization and communication protocols: HART, Profibus, Modbus, and wireless IoT integration.
High-reliability materials: For extreme environments (cryogenics, nuclear, aerospace).
Miniaturization: MEMS-based temperature transmitters for portable and wearable applications.
Smart features: Self-diagnosis, drift compensation, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
7. Conclusion
Temperature transmitters, as indispensable instruments, play a vital role in both industrial and everyday applications. From high-temperature metallurgical processes to precision control in consumer electronics, their versatility ensures a growing demand. With continuous innovation in materials, electronics, and digital integration, the scope of temperature transmitter applications will continue to expand.
