📖 Introduction
An Absolute Pressure Transmitter is a precision instrument designed to measure pressure relative to a perfect vacuum (zero absolute pressure). Unlike gauge pressure transmitters, which reference atmospheric pressure, absolute pressure transmitters use a sealed vacuum as the reference point. This makes them essential in applications where atmospheric pressure variations would otherwise affect accuracy.
These devices convert sensed pressure into an electrical output, such as a 4–20 mA current loop, voltage signal, or digital communication (e.g., HART protocol).
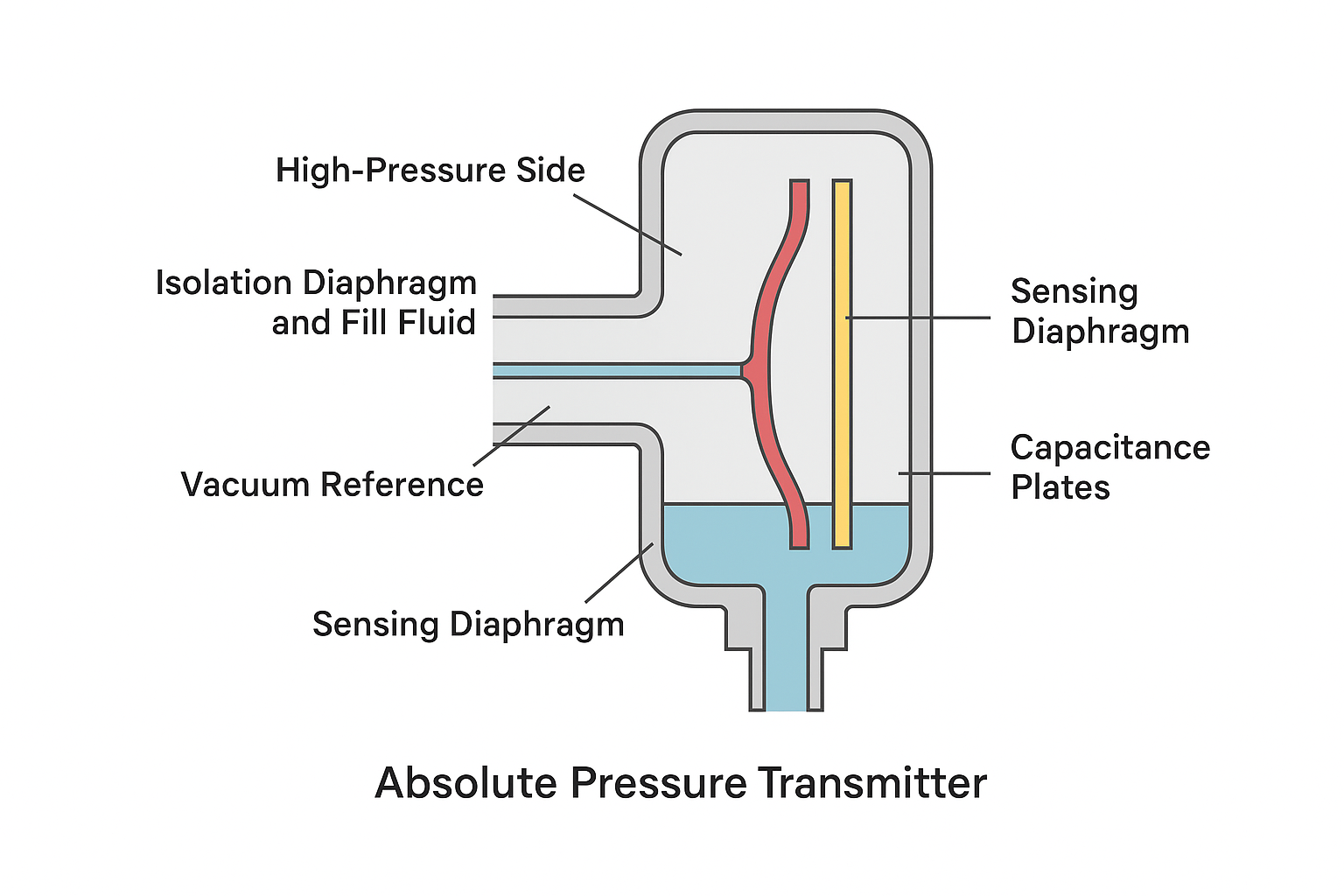
🛠️ Working Principle and Design
An absolute pressure transmitter consists of:
Isolation Diaphragms and Fill Fluid: Process pressure is applied to the high-pressure side of the device. A flexible diaphragm and fill fluid transmit this pressure to the sensor.
Vacuum Reference: The low-pressure side of the sensor is permanently sealed under high vacuum, providing a true zero reference point.
Sensing Element: A central diaphragm acts as a tensioned elastic element. Its displacement, proportional to applied pressure, is detected by differential capacitance plates.
Signal Conversion: Changes in capacitance are converted into electrical signals, enabling precise monitoring and control.
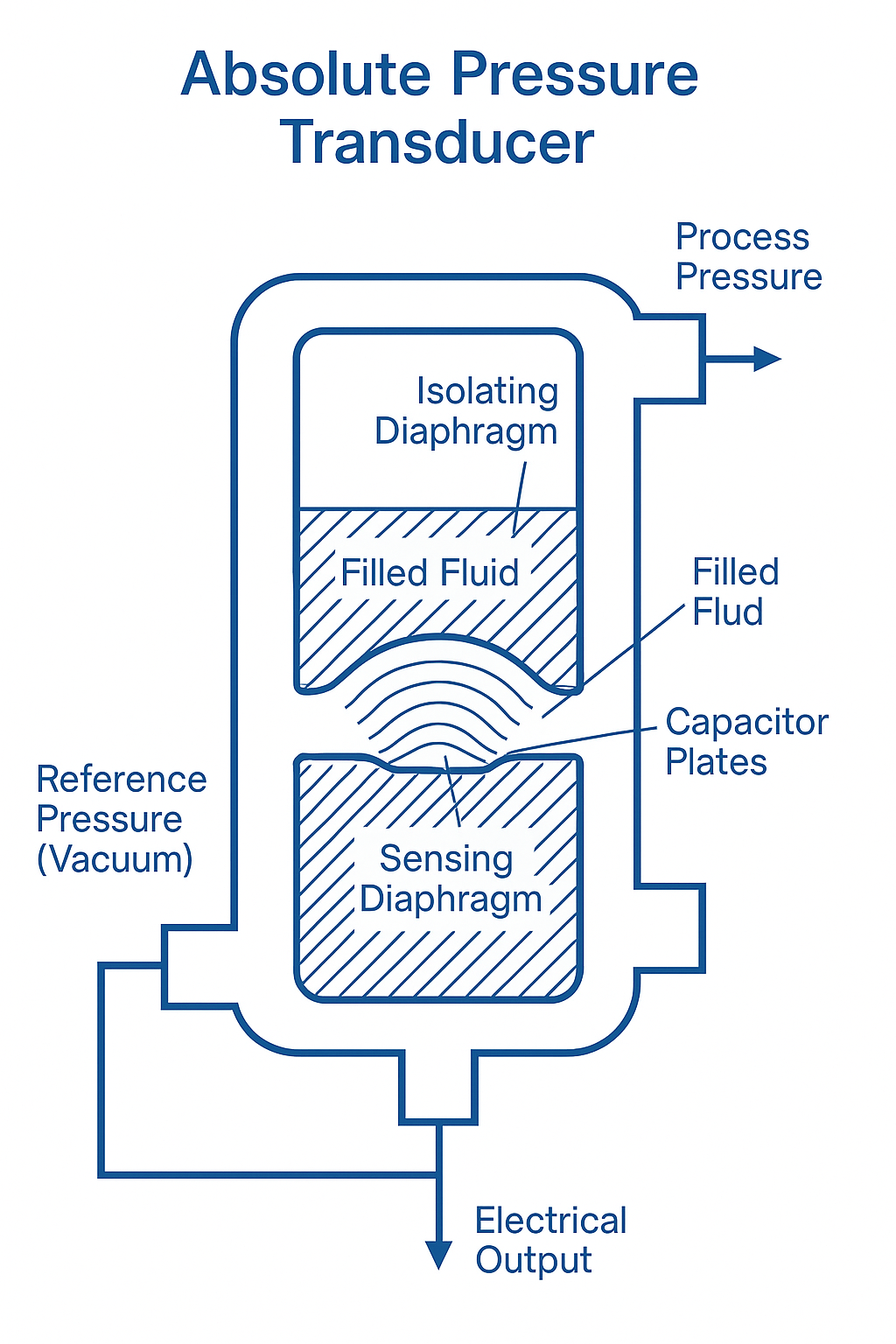
🎯 Zero Calibration Considerations
Zero calibration of absolute pressure transmitters requires special attention because the zero point represents a perfect vacuum (-100 kPa). In practice:
For applications requiring high accuracy, calibration must be performed under controlled vacuum conditions to establish a true zero.
Achieving a perfect vacuum in field conditions is challenging; therefore, factory calibration is recommended.
For moderate negative pressures (e.g., -10 to -20 kPa), gauge pressure transmitters may suffice if ultra-precise vacuum referencing is unnecessary.
🌐 Typical Applications
Absolute pressure transmitters are widely used in:
✔ Vacuum Systems: Semiconductor manufacturing, packaging processes.
✔ HVAC and Environmental Monitoring: Measuring barometric and room pressures.
✔ Industrial Process Control: Chemical reactors, distillation columns, and pharmaceutical production.
✔ Aerospace and Research: Altitude simulation and cryogenic systems.
📝 Summary
Absolute pressure transmitters provide reliable measurements relative to a true vacuum, making them indispensable for critical applications where precision is paramount. Understanding their working principles and calibration requirements ensures optimal performance and long-term reliability in industrial systems.
