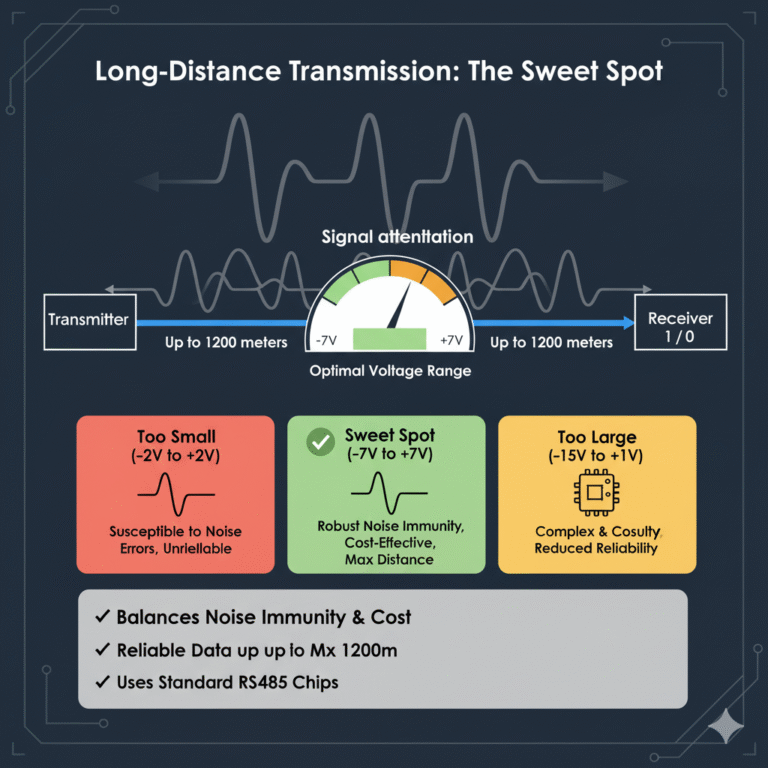
RS-485 is one of the most widely used serial communication standards in industrial automation, building control, and security systems. It uses differential signaling, which provides excellent noise immunity and allows multiple devices to share the same bus in a half-duplex topology.
Under ideal conditions, RS-485 communication can reach up to 1,200 meters, but actual distance is often limited by cable quality, baud rate, electromagnetic noise, and installation practices.
To maintain stable long-distance communication, engineers must take steps to reduce signal attenuation. Below are five practical and effective methods.
1. Use the Correct Cable Type
Choosing the right cable is fundamental for reliable RS-485 communication.
Use 120-ohm shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable to match the characteristic impedance of RS-485.
Twisted-pair wiring reduces common-mode noise.
Shielding must be properly grounded at one end to prevent ground loops.
Avoid thin conductors. Thicker wires have lower resistance, which reduces signal loss over long distances.
A properly selected cable can significantly improve transmission quality and noise immunity.

2. Reduce the Baud Rate for Long-Distance Communication
Baud rate and communication distance are inversely related:
Higher baud rate → Shorter transmission distance
Lower baud rate → Longer and more stable transmission
For example, reducing the baud rate from 115,200 bps to 9,600 bps can dramatically increase the reliable communication distance. When long-distance stability is required, always select the lowest acceptable baud rate for the application.
3. Use RS-485 Repeaters to Regenerate the Signal
As distance increases, the differential signal gradually weakens and degrades. Installing an RS-485 repeater helps:
Regenerate and reshape the signal waveform
Remove accumulated noise and distortion
Extend communication distance
A general guideline is to add a repeater every 800–1,000 meters, depending on installation conditions.
4. Install Proper Termination Resistors
To prevent signal reflection at the ends of the bus, install a 120-ohm termination resistor at each end of the RS-485 line.
Without proper termination:
The signal reflects at cable endpoints
Reflections overlap with the original signal
Data errors and communication instability occur
Correct termination ensures impedance matching and stable waveform integrity.
5. Ensure a Stable Power Supply for the RS-485 Driver
The RS-485 transceiver requires stable supply voltage to maintain proper differential output levels. Voltage drop along long cables or poor-quality power supplies may cause:
Reduced signal amplitude
Poor noise immunity
Intermittent communication failures
Use regulated power supplies and verify voltage levels at the device end, especially for long wiring distances.

Conclusion
Reliable RS-485 communication depends on proper cable selection, appropriate baud rate, use of repeaters, correct termination, and stable power supply.
By following these best practices, engineers can ensure long-distance, stable, and robust RS-485 communication suitable for industrial and automation environments.
