Electromagnetic flow meters are widely used in municipal water systems, industrial wastewater, chemical processing, food and beverage, metallurgy, and pharmaceutical industries. They offer stable measurement, no moving parts, and long service life.
However, the key to ensuring accuracy and reliability lies not in the instrument model, but in selecting the correct lining, electrode material, and structural configuration based on the medium and working conditions.
This article provides a clear and practical selection guide suitable for engineers, procurement teams, and system integrators.
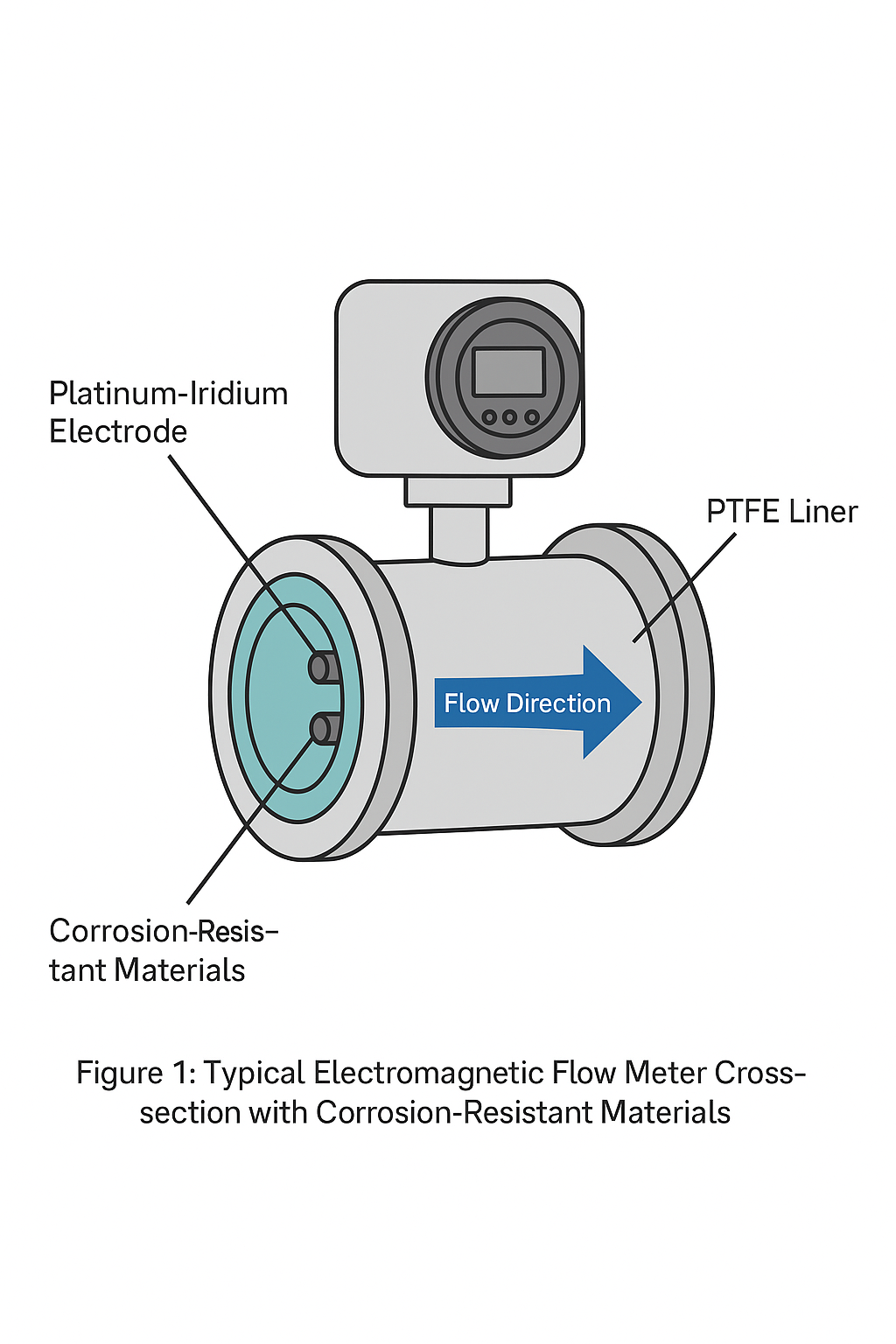
1. Core Principle of Selection
Selection = Medium Characteristics + Process Conditions + Application Requirements
Incorrect selection may lead to:
Measurement deviation (±5% or more)
Lining swelling or cracking
Electrode corrosion
Leakage and unplanned shutdowns
Correct selection ensures:
Accuracy: ±0.5% to ±1.0%
Stable long-term operation
Reduced maintenance and lifecycle cost
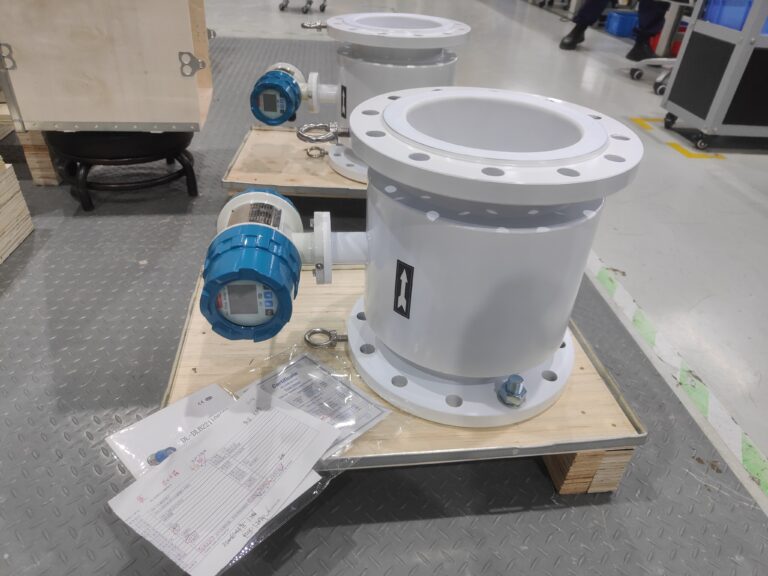

2. Essential Medium Information to Collect
Before selecting a meter, confirm the following parameters:
| Parameter | Reason | Typical Range / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition & concentration | Determines corrosion level | e.g., HCl with >0.5% fluoride ions requires special electrodes |
| pH value | Affects lining & electrode compatibility | pH < 2 or > 12 requires corrosion-resistant materials |
| Electrical conductivity | Must be ≥ 5 μS/cm | Pure water or solvents are not suitable |
| Solid particle content | Affects abrasion & lining type | Slurry >10% solids → high-wear lining required |
| Temperature range | High temperature limits lining options | PTFE ≤ 120°C, PFA ≤ 160°C, Ceramic ≤ 180°C |
| Pressure range | High temperature + high pressure coupling matters | Verify manufacturer pressure-temperature curve |
| Flow velocity | Impacts both accuracy and erosion | Recommended 1–3 m/s; >5 m/s accelerates wear |

3. Selecting the Lining Material
Priority logic: Corrosion > Temperature > Abrasion > Cost
| Lining Material | Temperature Limit | Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber (Neoprene / EPDM) | ≤ 80°C | Cost-effective, good for general water | Municipal water, cooling water |
| PTFE | ≤ 120°C | Excellent chemical resistance | Acid/alkali systems, chemical transfer |
| PFA | ≤ 160°C | High purity, low adsorption, high temp | Pharmaceutical, CIP/SIP environments |
| Polyurethane (PU) | ≤ 60°C | Strong abrasion resistance | Slurry, sand, ore pulp |
| Ceramic | ≤ 180°C | Excellent abrasion and corrosion resistance | Mining slurry, high-wear pipelines |
4. Selecting the Electrode Material
Electrodes must resist chemical attack while matching the lining’s thermal expansion behavior.
| Electrode Material | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Medium |
|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | General purpose | Clean water, weak acids/alkalis |
| Titanium (Ti) | Resistant to chloride ions | Seawater, salt solutions |
| Hastelloy C | Broad corrosion resistance | Mixed acids, pulp, chemical wastewater |
| Tantalum (Ta) | Very strong acid resistance | Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid |
| Platinum / Iridium Alloy | Extreme corrosion environments | Strong oxidizers or ultra-high purity fluids |
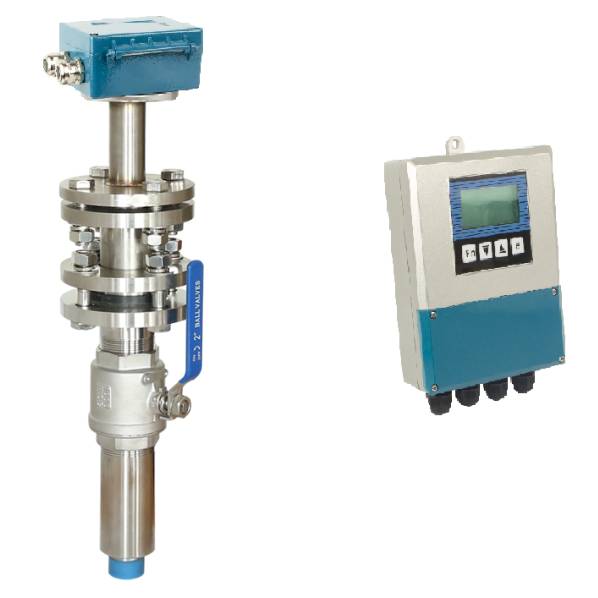

5. Application-Specific Selection Guidance
(1) Hot Water Systems (50–150°C)
Lining:
50–90°C → Rubber
90–130°C → PTFE
130–150°C → PFA or Ceramic (depending on pressure)Electrode:
316L for standard systems; Hastelloy C for chloride-rich water
(2) Food & Beverage (Juice, Milk, Syrup)
Requirements: hygienic design, smooth surface, no dead zones
Lining: FDA-compliant PTFE or PFA
Electrode: Polished 316L or Hastelloy C
Connection: Tri-clamp / sanitary flanges
(3) Pharmaceutical and Bioprocess (Sterile Liquids)
Requirements: CIP/SIP sterilization, 121–160°C steam exposure
Lining: High-purity PFA
Electrode: Hastelloy C
Design: SIP-resistant, dead-zone-free flow tube
(4) Mining Slurry / Abrasive Media
Lining: Polyurethane or Ceramic
Electrode: Tungsten carbide or Hastelloy
Installation: Keep velocity ≤ 3 m/s to reduce wear

6. Installation Recommendations
| Requirement | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Ensure a full pipe at measurement point | Avoids air bubbles affecting signal stability |
| Provide grounding rings or grounding electrodes | Ground resistance should be <10 Ω |
| Avoid installation near pumps or sharp elbows | Maintain straight run : 5D upstream / 3D downstream |
| For outdoor installation, add sun/rain protection | Prevent condensation and temperature shock |

7. Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
Inspect lining and electrodes every 3–6 months
Calibrate annually (trade measurement points → every 6 months)
Keep spare electrodes/liners in high-wear environments
Proper maintenance can extend service life by 30–50%.

Conclusion
The correct selection of an electromagnetic flow meter requires accurate understanding of the medium, careful matching of lining and electrode materials, and verification under actual process conditions.
A well-matched flow meter:
Ensures stable measurement
Reduces downtime
Minimizes total lifecycle cost
