1. Introduction
A Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) is a key device in industrial automation and remote monitoring systems. It converts physical signals into digital data and transmits them to the central control system. Within the RTU architecture, Input/Output (I/O) modules act as the critical bridge between field devices and the control center, enabling both data acquisition and command execution.
2. Input Functions: Signal Acquisition
The input section of an RTU I/O module collects and processes signals from field instruments. Typical categories include:
Analog Inputs (AI): Continuous signals such as temperature, pressure, flow, or level. Common formats are 4–20 mA current loops or 0–10 V voltage signals.
Digital Inputs (DI): Discrete signals indicating equipment status (e.g., ON/OFF, open/closed). Usually represented by high/low voltage levels or dry contacts.
Pulse Inputs: Counting signals for flowmeters, energy meters, or rotating equipment, used for recording frequency or accumulated volume.
Core role: Converting analog or digital signals into data that the RTU can interpret and upload to the supervisory control system.
3. Output Functions: Field Device Control
The output section connects to actuators and executes commands from the control system. Output forms include:
Analog Outputs (AO): Continuous control signals (current or voltage) for devices such as control valves and variable frequency drives.
Digital Outputs (DO): Discrete switching commands, e.g., motor start/stop, valve open/close.
Relay Outputs: Suitable for higher voltage/current switching, widely used for robust electrical control in industrial environments.
Design emphasis: Stability and fast response to ensure timely and reliable command execution.
4. Key Features of Modern RTU I/O Modules
With advances in industrial communication technology, modern I/O modules offer:
Modular Design: Flexible configuration of input/output channels, hot-swappable modules, easier maintenance and expansion.
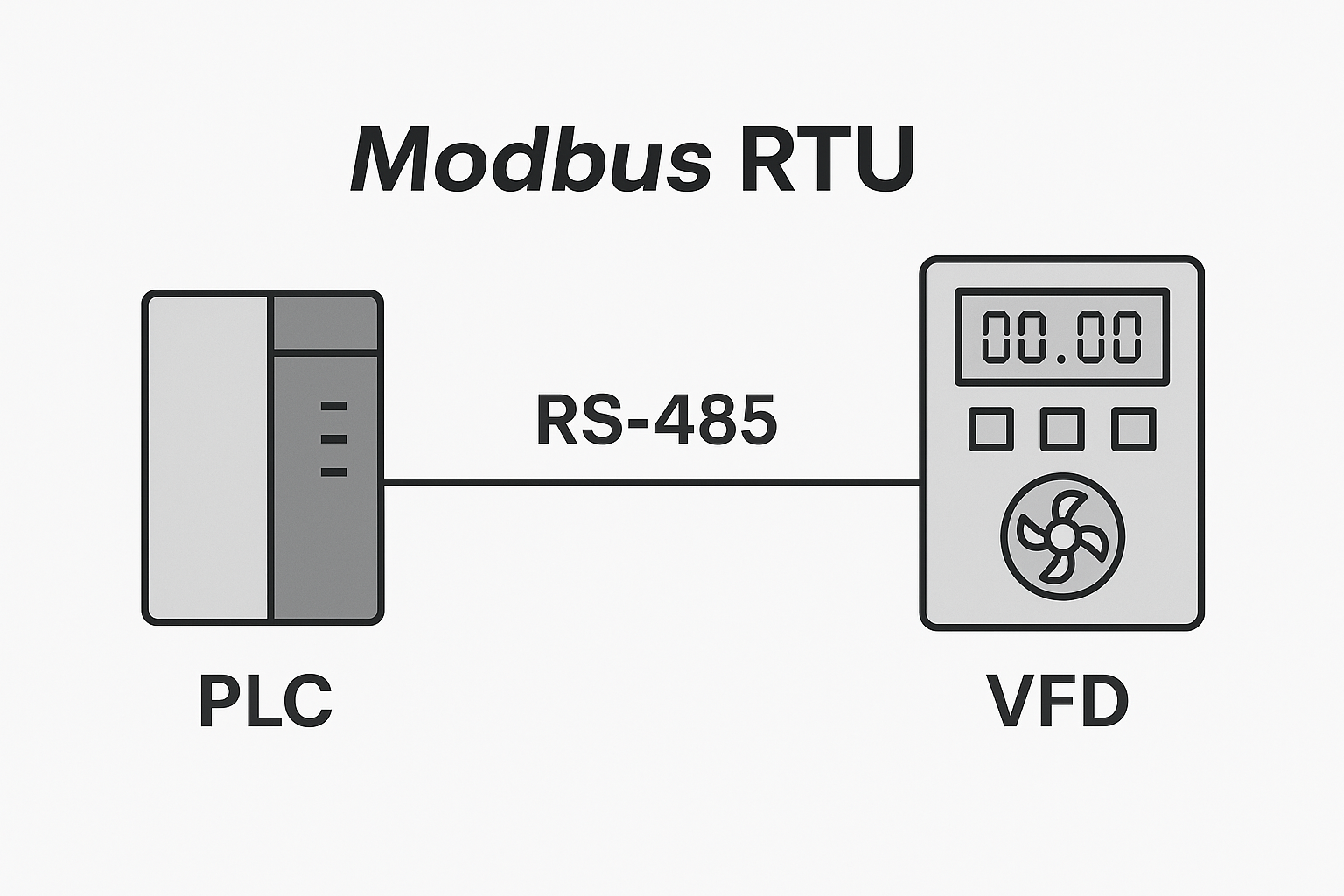
Multi-Protocol Compatibility: Support for Modbus, DNP3, IEC 60870, and other mainstream protocols for interoperability.
High Accuracy and Noise Immunity: Reliable signal conversion and robust EMC performance to suit harsh industrial environments.
Remote Diagnostics and Management: Advanced modules provide self-diagnosis and health monitoring to improve reliability and reduce downtime.
5. Application Scenarios
Water Treatment: AI acquires tank level data, DO controls pump start/stop.
Power Systems: DI monitors circuit breaker status, AO adjusts reactive power compensation devices.
Oil & Gas: Pulse inputs measure flow rates, relay outputs control emergency shutdown valves.
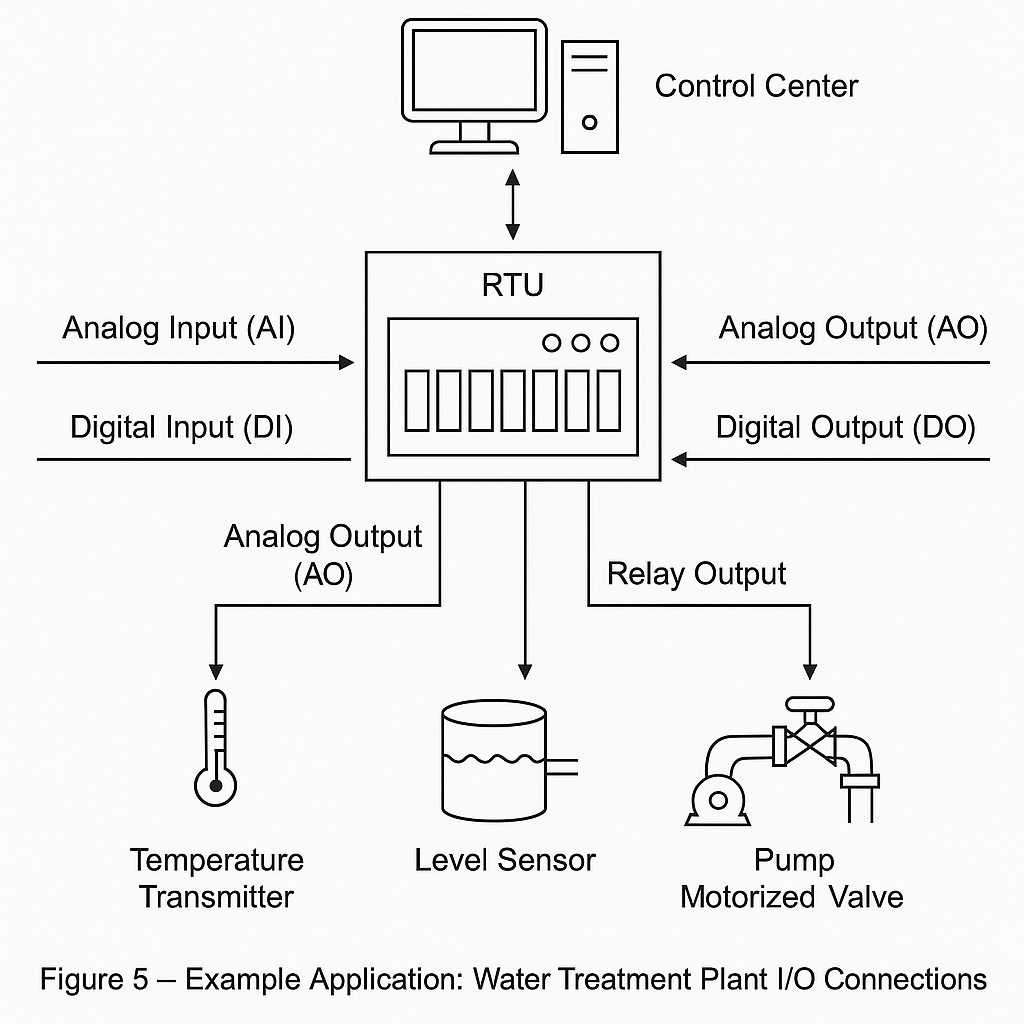
6. Conclusion
The I/O module is the nerve center of the RTU, linking field devices with control logic. From signal acquisition to actuator control, it ensures that industrial processes remain reliable, efficient, and responsive.
