Abstract
In modern process industries, most equipment and system failures can be traced back to a limited set of underlying causes. This article summarizes the seven most common factors that affect industrial automation and control systems, explains their impact, and provides recommended countermeasures for engineers and maintenance teams.
1. Measurement Signal Problems
Accurate measurement is the cornerstone of automatic control. In process industries, materials often have flammable, corrosive, or toxic properties, making online measurement difficult. Many critical parameters—such as composition or quality indices—may only be obtained via laboratory sampling, causing delays and inaccuracies.
Impact: Feedback control systems rely heavily on accurate signals. Measurement errors directly lead to poor control performance.
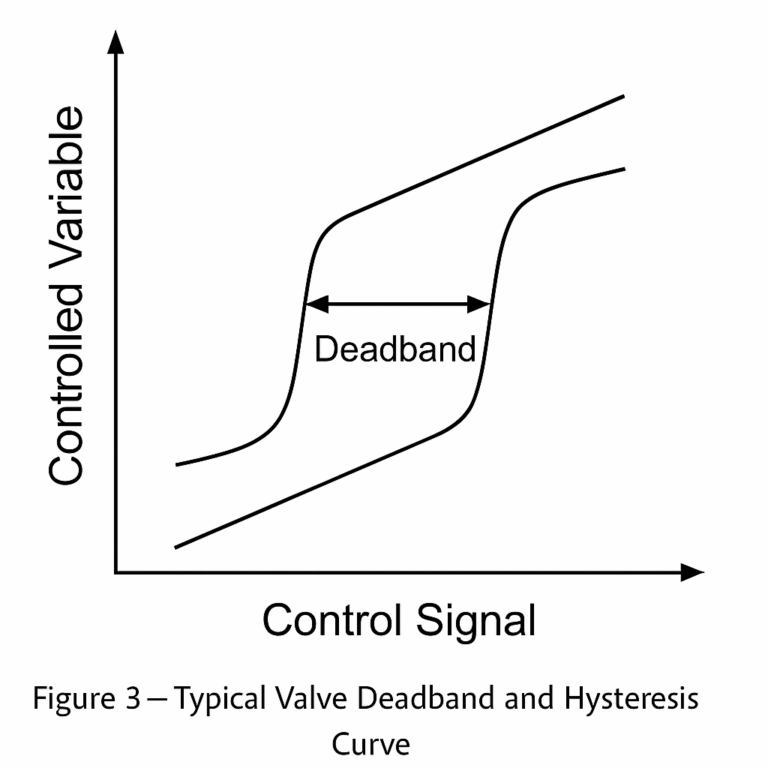
2. Actuator Characteristics
Actuators, such as control valves, are responsible for executing the controller’s commands. Their static and dynamic characteristics—including hysteresis, deadband, and response speed—have a direct influence on system stability and accuracy.
Impact: Poor actuator performance can lead to sluggish responses, oscillations, or even instability.
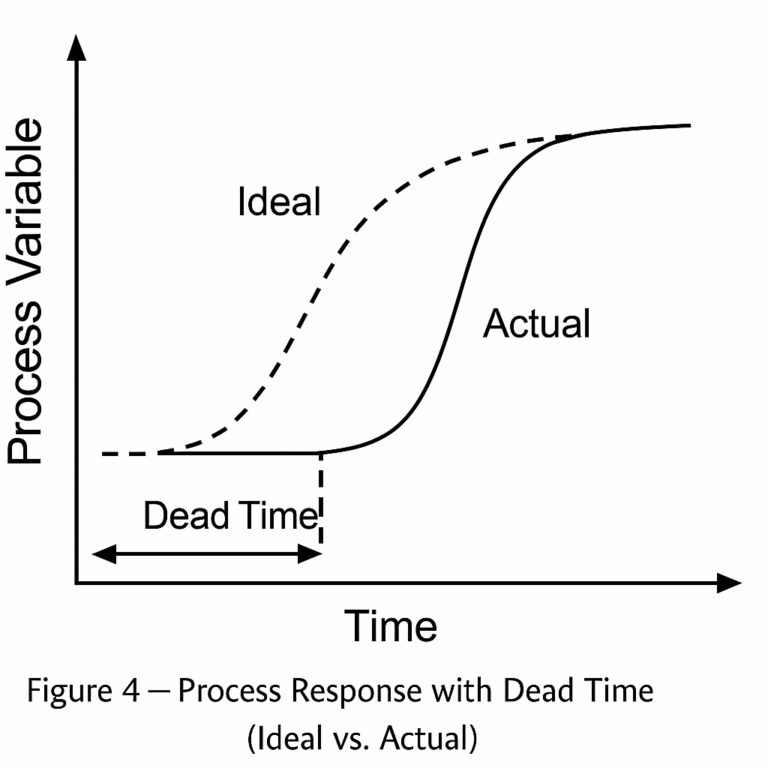
3. Process Dead Time (Time Delay)
Controlled processes often contain inherent delays. For example, temperature control in large furnaces shows significant dead time compared to flow control in pipelines.
Impact: Longer dead time reduces the system’s ability to respond quickly, leading to overshoot and degraded control quality.
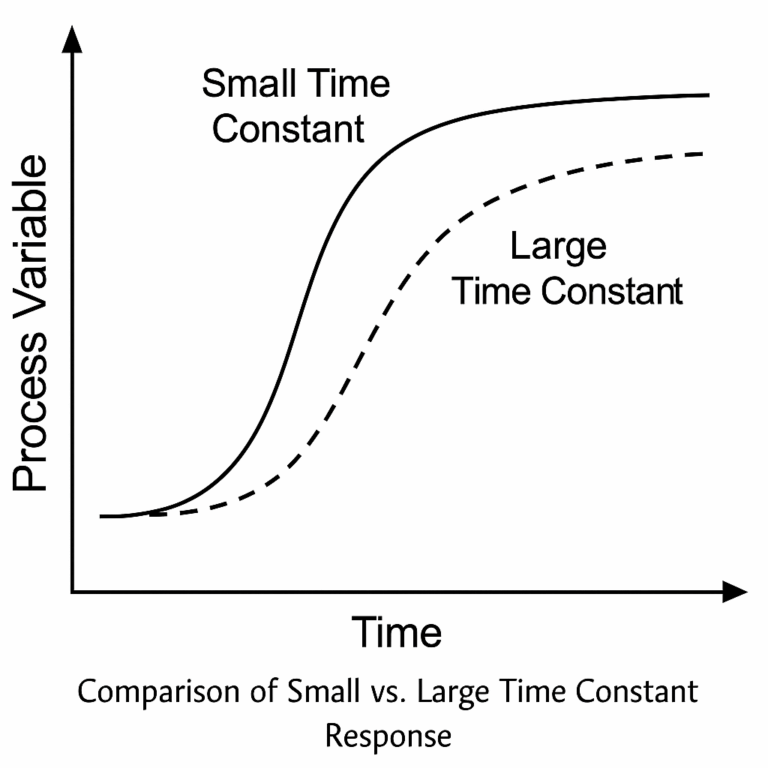
4. Differences in Process Time Constants
Different processes have varying time constants. For instance, flow control loops respond within seconds, while heating processes may take minutes or hours to stabilize.
Impact: Large time constants limit control precision and require careful tuning of controller parameters.
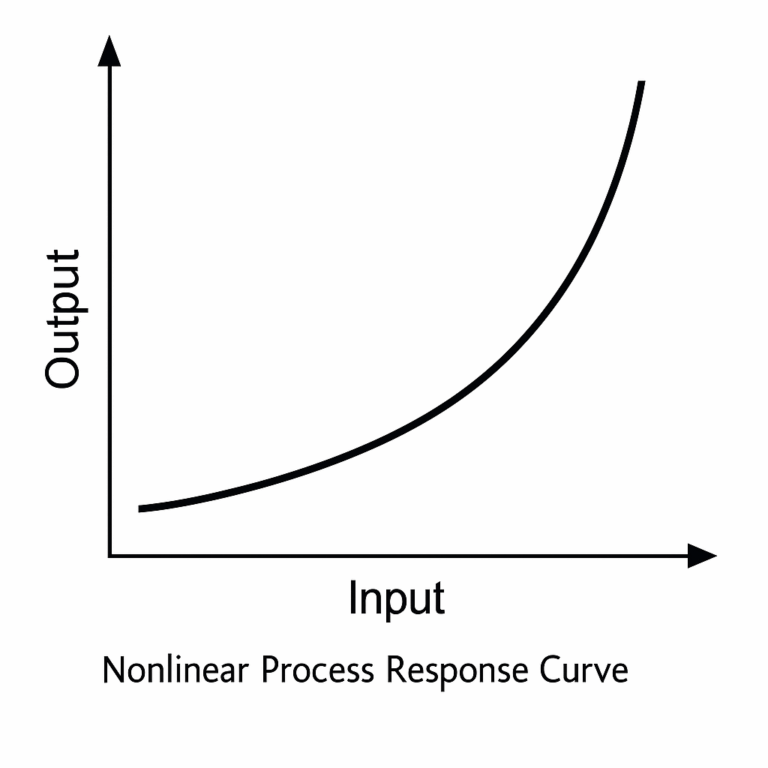
5. Nonlinear Characteristics
Most industrial processes are inherently nonlinear. Their responses to control actions or disturbances vary across different operating ranges.
Impact: Nonlinearity makes it difficult for traditional PID control to maintain optimal performance across all conditions.
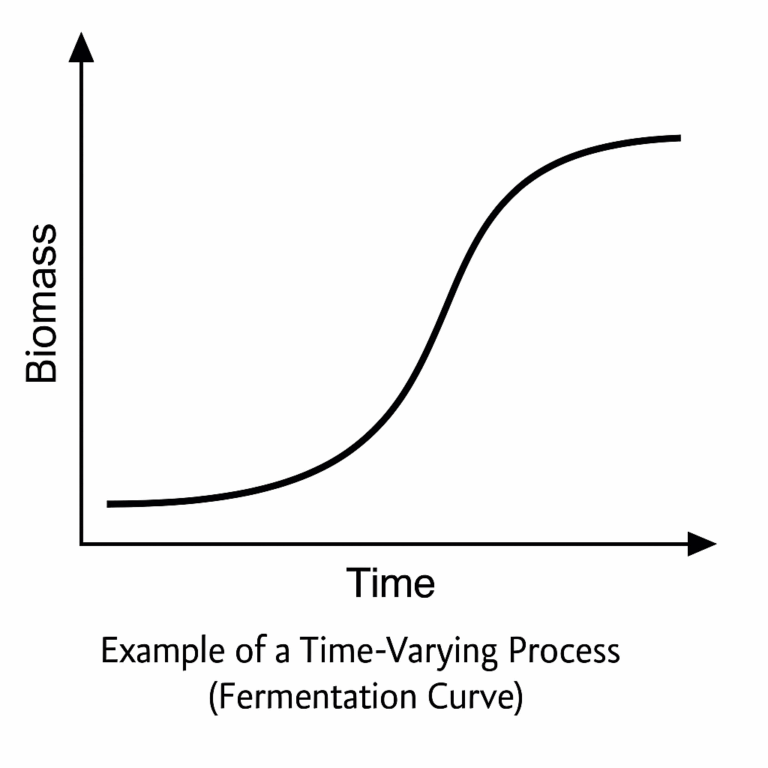
6. Time-Varying Nature
Some processes, such as biological fermentation, change significantly over time. Biomass concentration, raw material consumption, and product formation are all time-dependent.
Impact: Time-varying processes require adaptive or advanced control strategies; otherwise, system performance deteriorates.
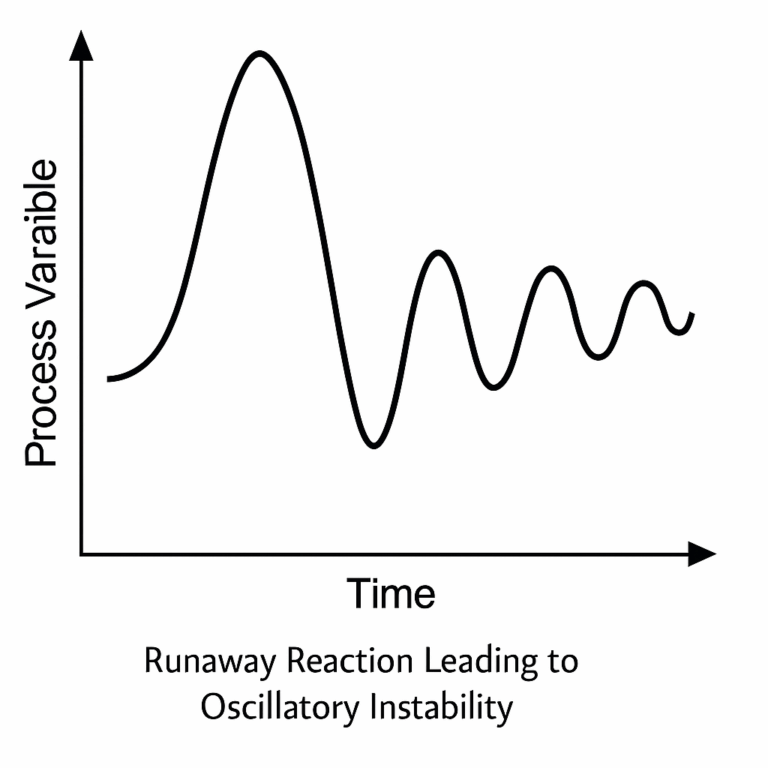
7. Inherent Instability
Certain chemical and biochemical processes are unstable under specific operating conditions. For example, runaway reactions can cause exponential increases in temperature and pressure.
Impact: Once the process enters an unstable region, automatic control may lose effectiveness, and oscillations or accidents can occur.
Summary Table: Causes, Symptoms, and Countermeasures
| Root Cause | Typical Symptoms | Recommended Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Signal Problem | Drift, false readings, delayed signals | Redundant sensors, periodic calibration, signal filtering |
| Actuator Issues | Valve sticking, slow response | Use high-quality actuators, regular maintenance |
| Process Dead Time | Delayed control action, overshoot | Feedforward control, Smith predictor, PID optimization |
| Large Time Constants | Slow stabilization, sluggish loops | Adjust controller tuning, use cascade control |
| Nonlinear Characteristics | Inconsistent performance across ranges | Gain scheduling, model predictive control (MPC) |
| Time-Varying Nature | Performance degradation over time | Adaptive control, frequent re-tuning |
| Inherent Instability | Oscillations, runaway conditions | Safety interlocks, SIS protection, advanced control logic |
Conclusion
While industrial failures may appear diverse and complex, nearly all of them can be traced back to these seven fundamental causes. By improving measurement accuracy, actuator performance, control strategies, and stability safeguards, engineers can significantly reduce failure risks and enhance process reliability.
