This guide explains how to choose the installation height for combustible or toxic gas detectors based on whether the leaking gas is heavier or lighter than air. It also includes a special note for oxygen (O₂) sensors.
1) Classify the gas by buoyancy (relative to air)
Let N = (gas molecular weight) / 29, where 29 is the average molecular weight of air.
Use the following thresholds:
Heavy: N ≥ 1.2
Slightly heavy: 1.0 ≤ N < 1.2
Slightly light: 0.8 < N < 1.0
Light: N ≤ 0.8
Quick references (relative molecular weight): H₂ = 2, CO = 28, N₂ = 28, O₂ = 32, HCl = 36.5; Air ≈ 29 (e.g., 78% N₂, 21% O₂).
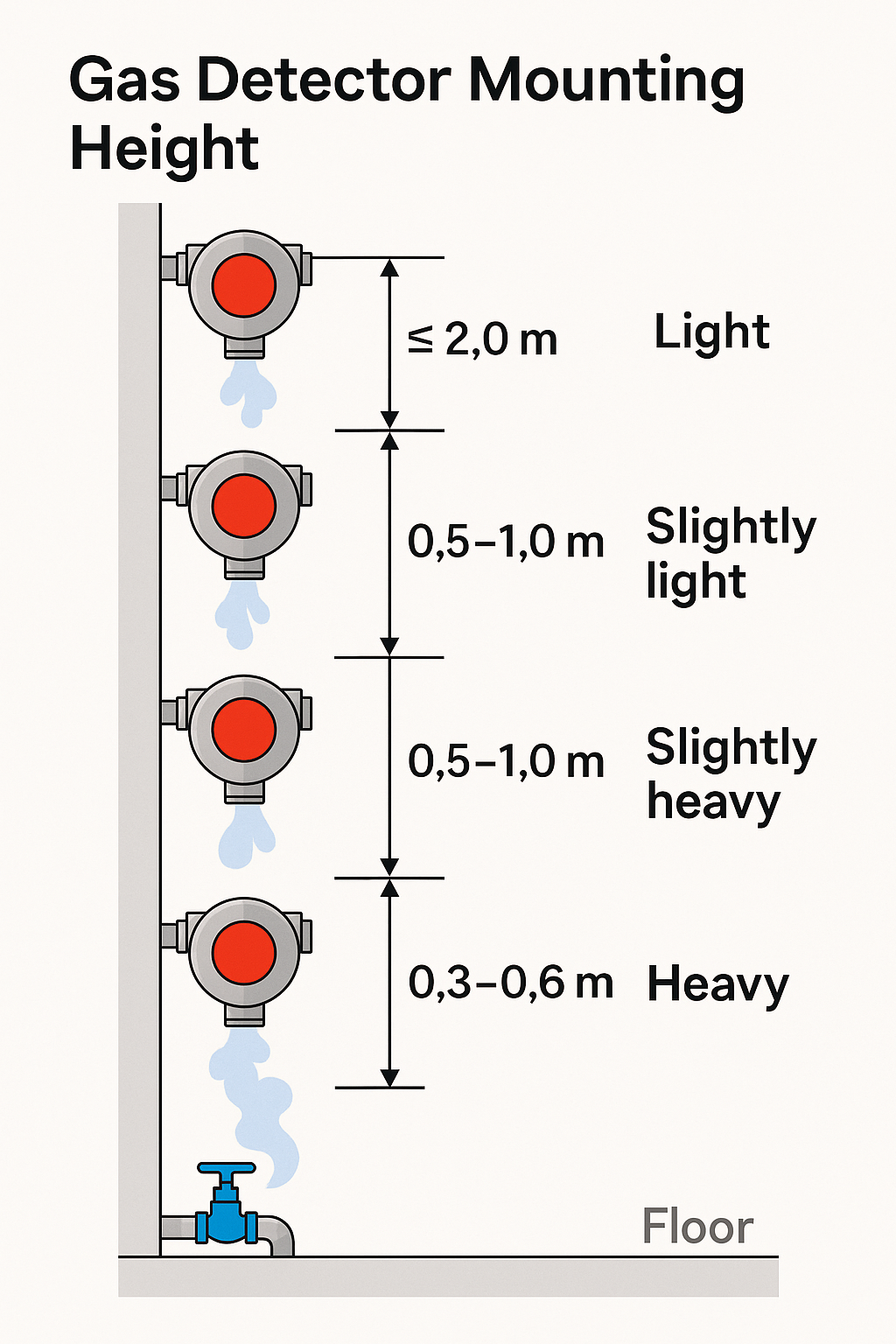
2) Recommended detector height by gas class
| Gas class | Typical behavior | Mounting height rule |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy (N ≥ 1.2) | Tends to sink and accumulate near the floor | 0.3–0.6 m above floor (finished floor level) |
| Slightly heavy (1.0 ≤ N < 1.2) | Drifts downward from the leak point | 0.5–1.0 m below the release source |
| Slightly light (0.8 < N < 1.0) | Drifts upward from the leak point | 0.5–1.0 m above the release source |
| Light (N ≤ 0.8) | Rises quickly and stratifies aloft | Within 2.0 m above the release source |
“Release source” means the likely leak location (e.g., valve stem, pump seal, flange, process vent). Choose the height relative to that point.
3) Special case — Oxygen (O₂) sensors
Mount at 1.5–2.0 m above floor (typical breathing zone for personnel monitoring).

4) How to use this in practice
Compute N: divide the gas molecular weight by 29.
Pick the class using the thresholds above.
Place the detector at the corresponding height rule relative to the floor or release source.
Refine placement with site specifics:
Avoid dead air pockets (corners, behind equipment).
Consider ventilation direction and speed; detectors should be in the probable gas path.
Keep clear of heat sources or high humidity that could affect sensing.
Maintain service access (calibration gas reach, visual access).
For mixed or uncertain gases, consider multiple heights or a small array near the source.
5) Fast examples
Propane (C₃H₈, MW ≈ 44): N ≈ 44/29 ≈ 1.52 → Heavy → mount 0.3–0.6 m above floor.
Carbon monoxide (CO, 28): N ≈ 0.97 → Slightly light → 0.5–1.0 m above the leak point.
Hydrogen (H₂, 2): N ≈ 0.07 → Light → within 2.0 m above the release source.
