Vortex flow meters are trusted for steam flow measurement due to their robustness, high-temperature tolerance, and low maintenance. But like any instrument, they can face problems in real-world applications. This guide walks you through typical problems, their causes, and practical solutions, especially in steam service.
🛠️ Issue 1: No Flow Signal or Constant Zero Output
Possible Causes:
Flow is too low to generate vortices.
Sensor cable disconnected or broken.
Sensor electronics failure.
Recommended Fix:
Verify actual steam flow rate and compare to meter’s minimum range.
Inspect and reconnect wiring.
Check power supply to transmitter.
Replace sensor if necessary.
📌 Tip: Most vortex meters require a minimum Reynolds number (~10,000+) to generate a stable signal.
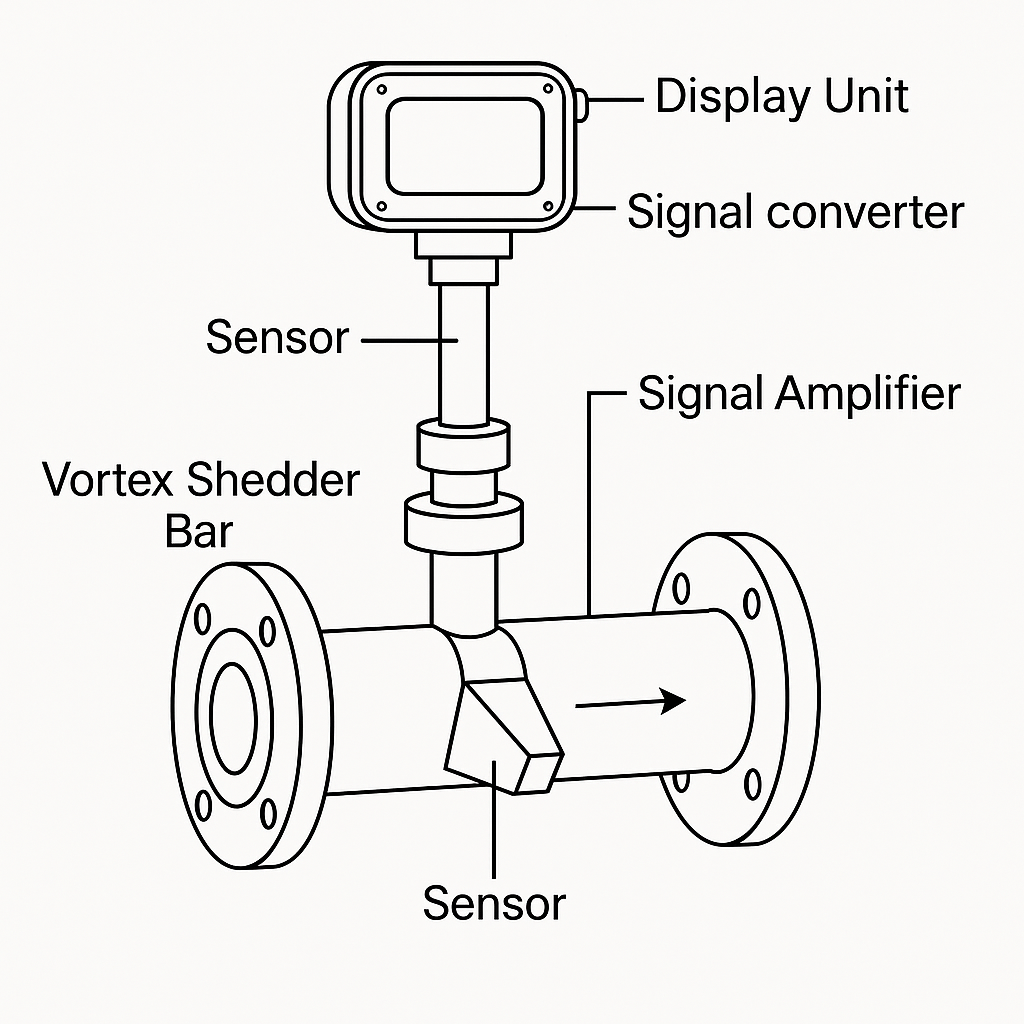
⚠️ Issue 2: Fluctuating or Unstable Readings
Possible Causes:
Excessive pipeline vibration.
Wet steam or condensate passing through meter.
Air pockets or inconsistent flow.
Recommended Fix:
Add pipe supports or vibration dampers.
Install upstream steam traps and drip legs.
Purge air during startup.
Avoid installing meter at low points or elbows.
💡 Insight: Use mechanically isolated meters or vibration-compensated designs in dynamic piping.
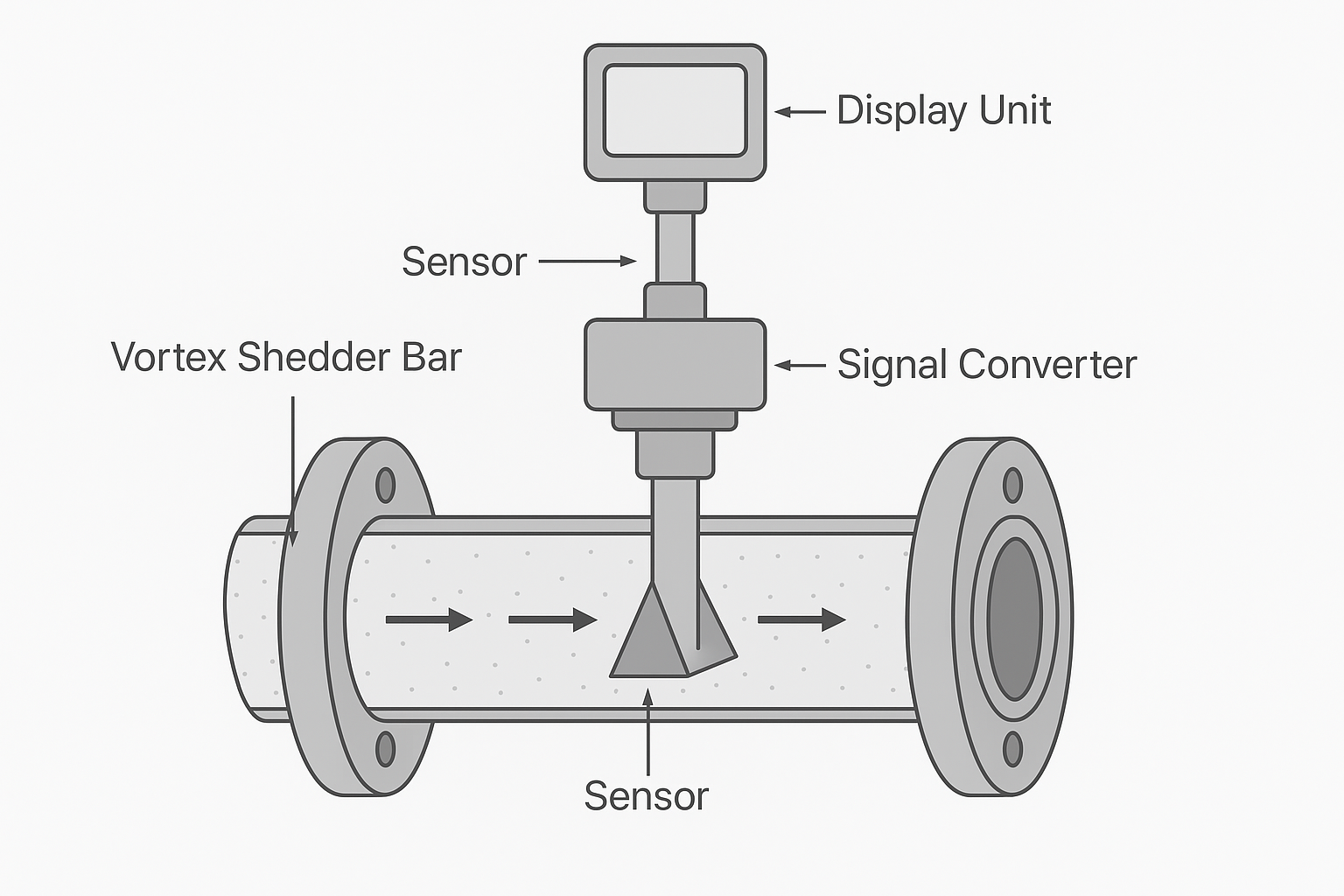
📉 Issue 3: Sudden Drop in Output Signal
Possible Causes:
Blocked bluff body due to debris.
Damage to internal sensor element.
Valve partially closed upstream.
Recommended Fix:
Shut off flow and inspect bluff body for blockage.
Use inline strainer to prevent foreign material.
Perform continuity test on signal lines.
Check upstream valve status.

🔄 Issue 4: Signal Spikes or False Pulses
Possible Causes:
Moisture droplets or condensate hitting sensor.
Electrical noise from nearby power equipment.
Improper grounding or shielding.
Recommended Fix:
Improve steam dryness.
Ensure cable shielding is grounded at one end only.
Re-route signal cable away from power lines or VFDs.
🔌 Tip: Use twisted-pair, shielded signal cables with high-quality connectors.

🔎 Issue 5: Output Too High or Low (Compared to Actual Flow)
Possible Causes:
Incorrect meter factor or configuration.
Flow profile distortion due to upstream fittings.
Software offset or zero shift.
Recommended Fix:
Recheck meter settings (K-factor, units, damping time).
Confirm correct straight pipe lengths.
Recalibrate meter or perform zero reset procedure.
📋 Reminder: Some meters offer automatic zeroing—ensure done with no flow present.

🔧 Commissioning Checklist to Prevent Errors
Before starting up the system, make sure:
✅ Flow direction matches arrow on meter.
✅ Pipe is full of steam, no air or condensate.
✅ Straight-run piping is sufficient.
✅ Signal cables are wired correctly.
✅ Sensor is properly grounded.

📌 Conclusion
Troubleshooting vortex flow meters doesn’t need to be difficult. Most issues relate to installation, steam quality, or electrical setup. By following this guide, you can quickly identify root causes and apply targeted fixes—saving time, money, and steam.
