Abstract:
Metrological calibration plays a critical role in ensuring product quality and process compliance. In modern manufacturing and instrumentation environments, two common approaches are adopted: internal calibration (in-house) and external calibration (third-party). This article presents a comprehensive comparison between the two methods, helping manufacturers optimize their calibration strategies.
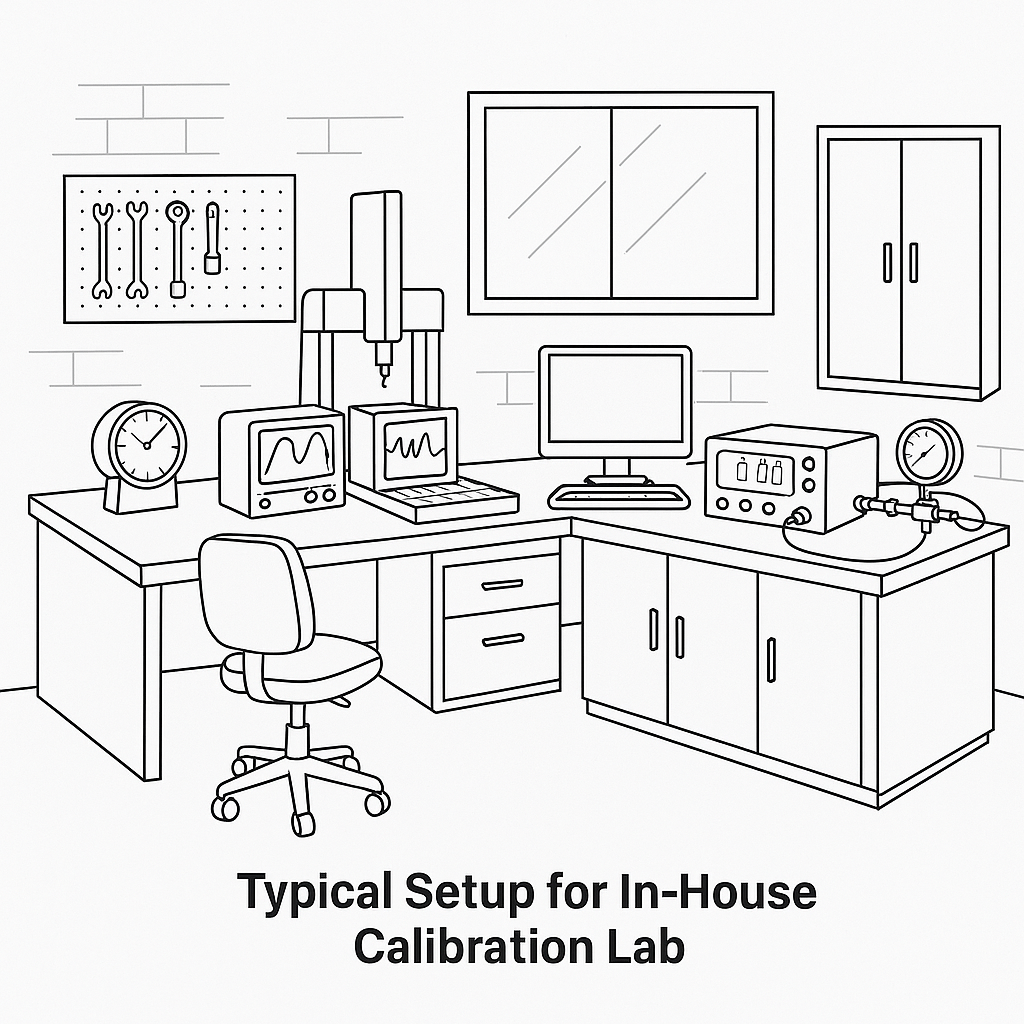
1. Internal Calibration and Inspection (In-House)
Definition:
Internal calibration is conducted by a company’s own technicians using in-house tools and equipment. It is typically integrated into routine quality control and production processes.
Key Characteristics:
Fast response time: Ideal for handling on-site deviations and process adjustments in real-time.
High flexibility: Can be performed as needed, depending on production requirements.
Cost-effective in the long run: Although initial investment in equipment is high, it reduces recurring service expenses.
Technical expertise required: Requires well-trained personnel and proper documentation systems.
Typical Applications:
Real-time quality control in manufacturing lines.
Calibration of process instruments such as pressure transmitters or flow meters.
Preparation for internal audits or certifications.
Illustration 1: Typical Setup for In-House Calibration Lab
2. External Calibration and Inspection (Third-Party Services)
Definition:
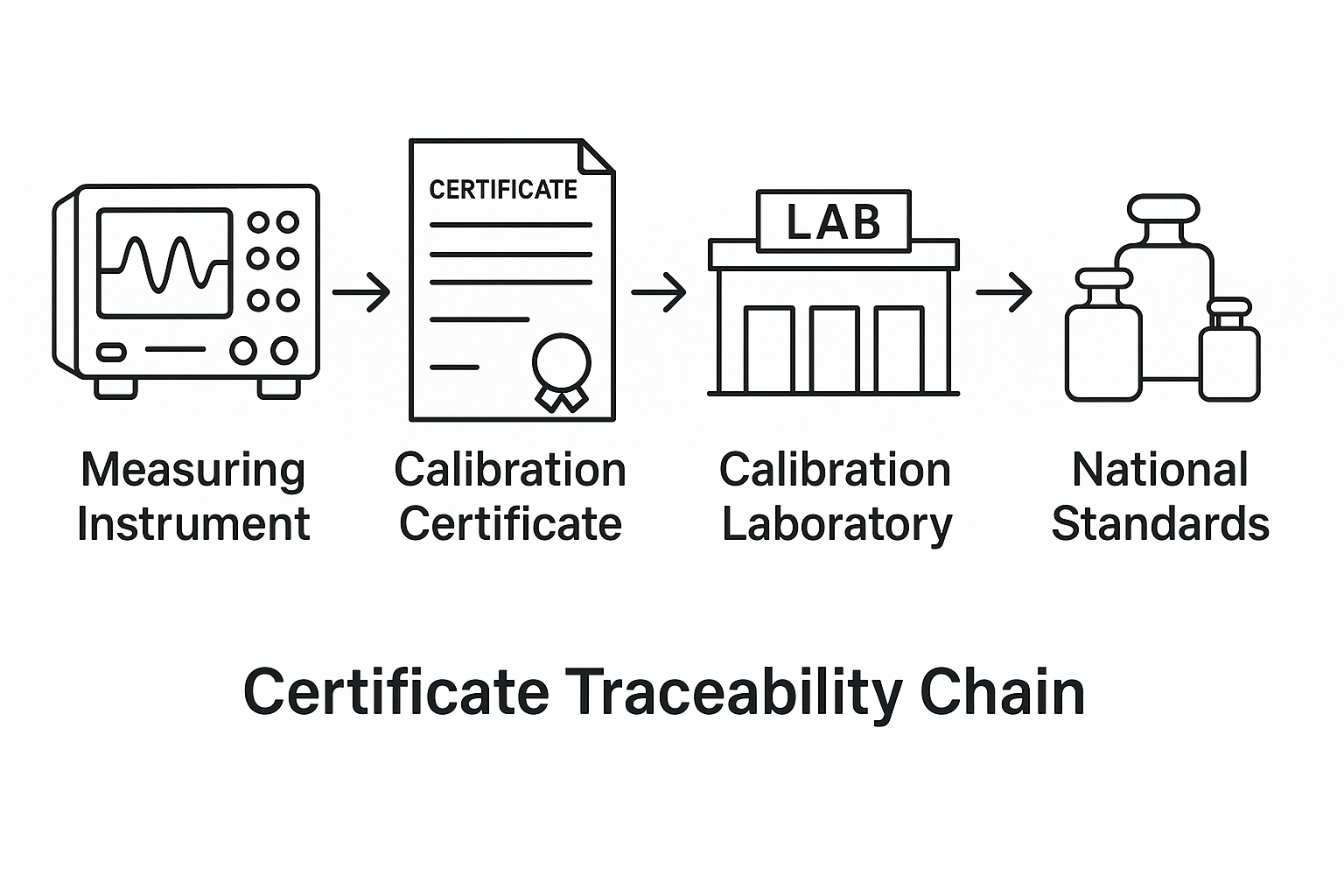
External calibration refers to services performed by certified metrology labs that comply with recognized standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 17025, CNAS, ILAC).
Key Characteristics:
High credibility: Required in cases where traceable documentation is legally or contractually mandated.
Standardized traceability: Calibration results are traceable to national or international standards.
Suitable for high-precision applications: Especially in sectors like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and legal metrology.
Longer lead time & higher cost per event: Due to logistics, handling, and service charges.
Typical Applications:
Annual mandatory inspections.
Export products requiring certified calibration reports.
Client or regulatory compliance checks.
Illustration 2: Certificate Traceability Chain for Third-Party Calibration
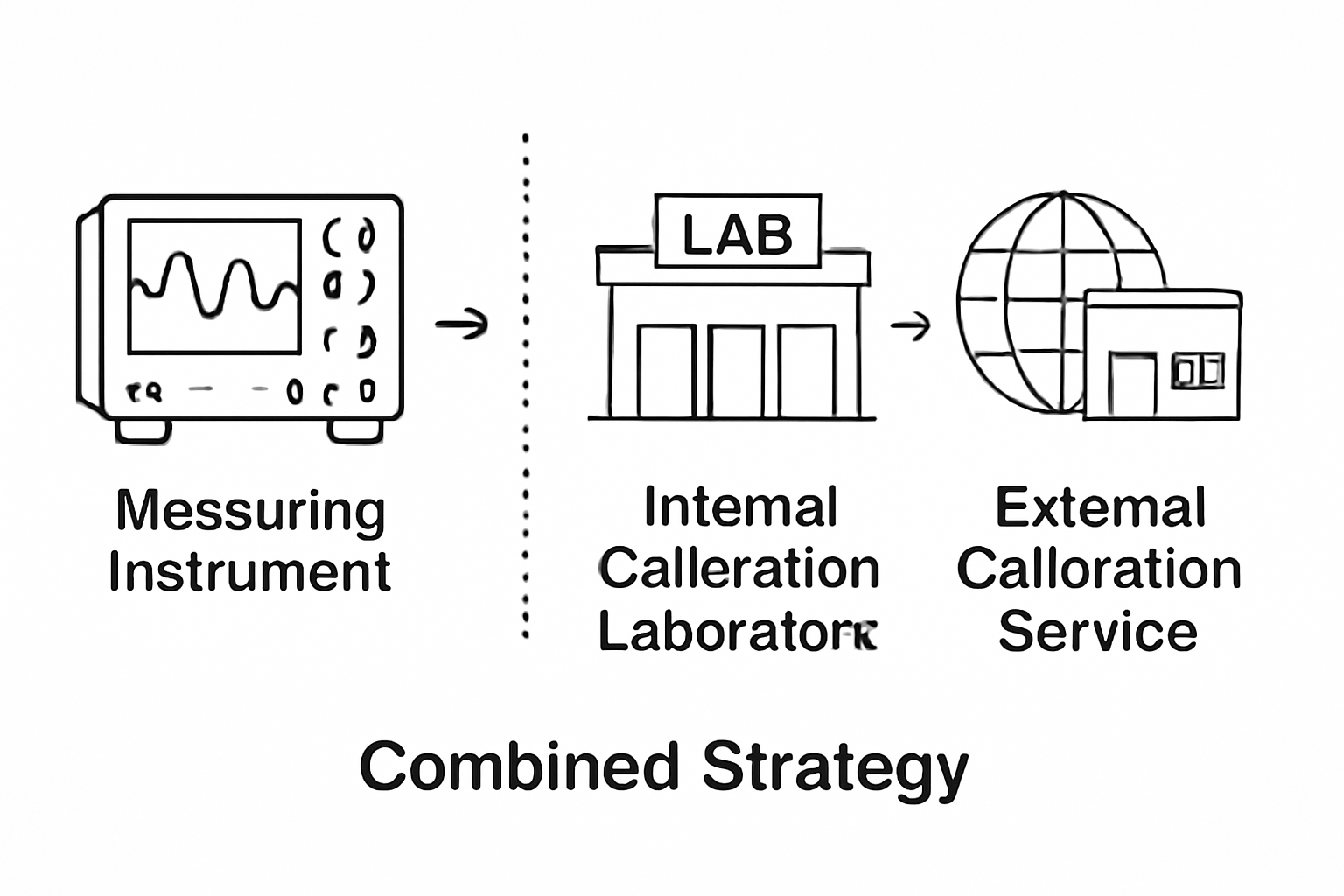
4. Conclusion
Both internal and external calibration methods are valuable components of a robust quality system. A hybrid approach—internal daily control combined with scheduled external verification—can help manufacturers achieve cost-efficiency, legal compliance, and superior product quality simultaneously.
Illustration 3: Recommended Hybrid Calibration Strategy Flowchart