Stainless steel, known for its excellent overall performance and aesthetic surface characteristics, is widely used in various industries—including in level instruments and fluid transport systems. Among its many forms, stainless steel pipes are the most commonly applied components.
These pipes can be broadly categorized into two types: seamless stainless steel pipes and welded stainless steel pipes. Understanding their differences is crucial for proper selection and economic application.

I. Key Differences Between Seamless and Welded Stainless Steel Pipes
1. Manufacturing Process
Welded Pipes: Manufactured by rolling stainless steel plates or strips and welding the seam using processes such as ERW (Electric Resistance Welding) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding. The inner surface typically has a visible longitudinal weld line.
Seamless Pipes: Produced from solid round billets that are pierced through the center and then processed using hot extrusion, cold drawing, or cold rolling. No welding seam is present.
2. Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy
Welded Pipes:
High dimensional accuracy
Uniform wall thickness
Smooth internal and external surfaces
Available in thinner wall versions for lightweight applications
Seamless Pipes:
Lower precision in wall thickness and diameter
Surfaces may have minor imperfections such as scale, pitting, or oxide spots
Generally thicker wall designs
3. Mechanical Properties and Cost
Seamless Pipes offer superior performance in:
Pressure resistance
High-temperature strength
Corrosion resistance
Welded Pipes, with improved welding techniques, now approach the strength of seamless types in many low-pressure applications.
Cost Comparison:
Seamless pipes are more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes.
Welded pipes are more economical for large-volume and non-critical applications.
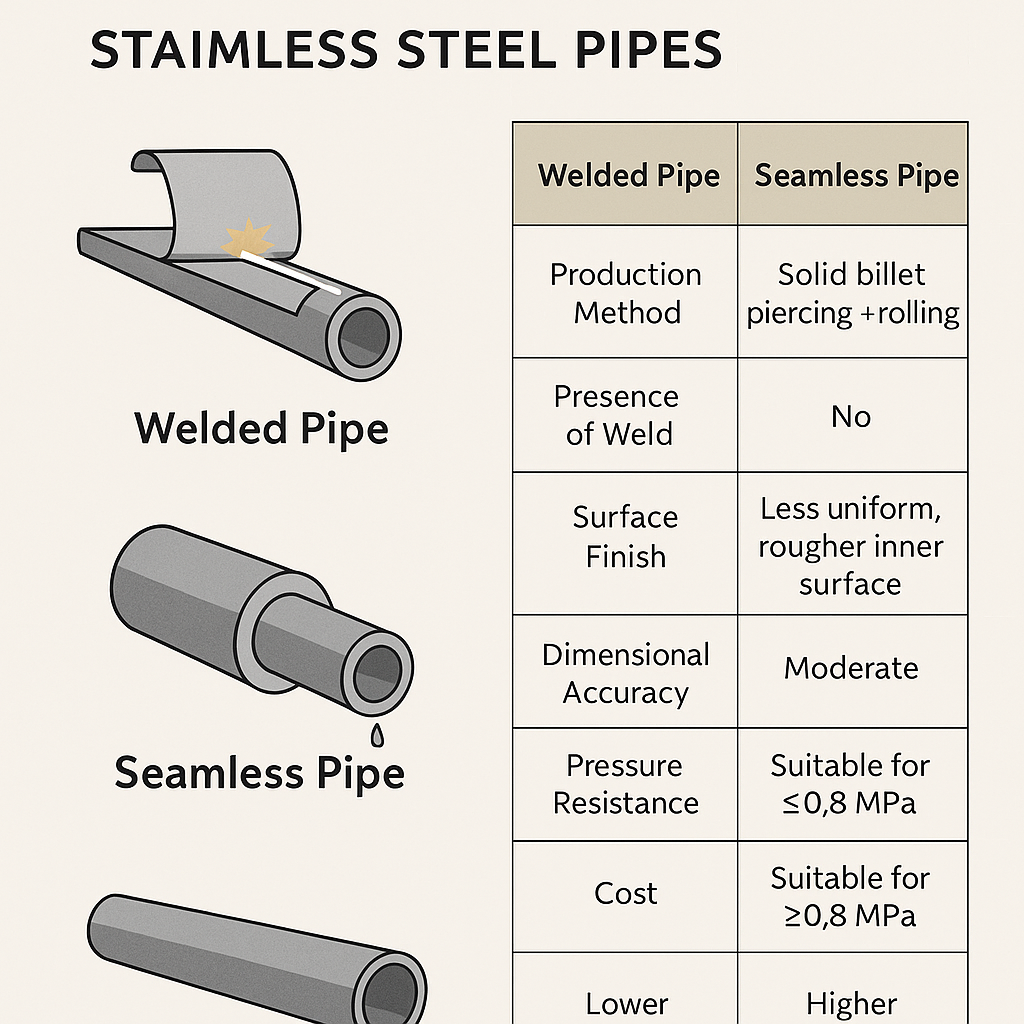
📊 Comparison Table: Seamless vs. Welded Stainless Steel Pipes
| Feature | Welded Pipe | Seamless Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Plate/strip rolling + welding | Solid billet piercing + rolling |
| Presence of Weld | Yes | No |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and uniform | Less uniform, rougher inner surface |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High | Moderate |
| Wall Thickness Tolerance | Narrow | Variable |
| Pressure Resistance | Suitable for ≤0.8 MPa | Suitable for ≥0.8 MPa |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Availability of Thin-Wall Option | Yes | Rare |
II. Selection Guidelines for Practical Applications
To achieve the best balance between performance, appearance, and cost-effectiveness, consider the following selection criteria:
For Decorative and Display Use
Choose welded stainless steel pipes for applications requiring high surface finish—e.g., architectural elements, handrails, display fixtures, etc.For Low-Pressure Fluid Transport
Welded pipes are suitable for conveying water, oil, compressed air, natural gas, and heating steam in systems operating below 0.8 MPa.For High-Temperature or High-Pressure Applications
Seamless pipes are essential in industrial fluid pipelines, especially in:Petrochemical plants
Power stations
Boiler systems
Nuclear facilities
Economic Consideration
When the pressure is within a safe range and the environment is not corrosive, welded pipes are often preferred due to their lower cost.
✅ Conclusion
Understanding the core differences between seamless and welded stainless steel pipes is crucial in optimizing your project’s reliability and budget. Seamless pipes offer superior performance for harsh environments, while welded pipes are more cost-effective and widely applicable in non-critical systems.
