In industrial process automation, control valves are among the most important final control elements. Valve positioners—especially smart electro-pneumatic types—play a vital role in improving control accuracy, response speed, and system efficiency.
Smart valve positioners can be classified by their I/P converter mechanisms into two main types: nozzle-flapper and piezoelectric valve. Leading global manufacturers use different structures. For instance:
Piezoelectric I/P: Siemens SIPART PS2, Metso ND9000
Nozzle-Flapper I/P: Emerson Fisher DVC6200, SAMSON 3730-3, Azbil AVP300
These two types differ significantly in working principle, structural design, energy efficiency, control performance, and applicable scenarios. This article presents a detailed comparison.
1. Working Principle
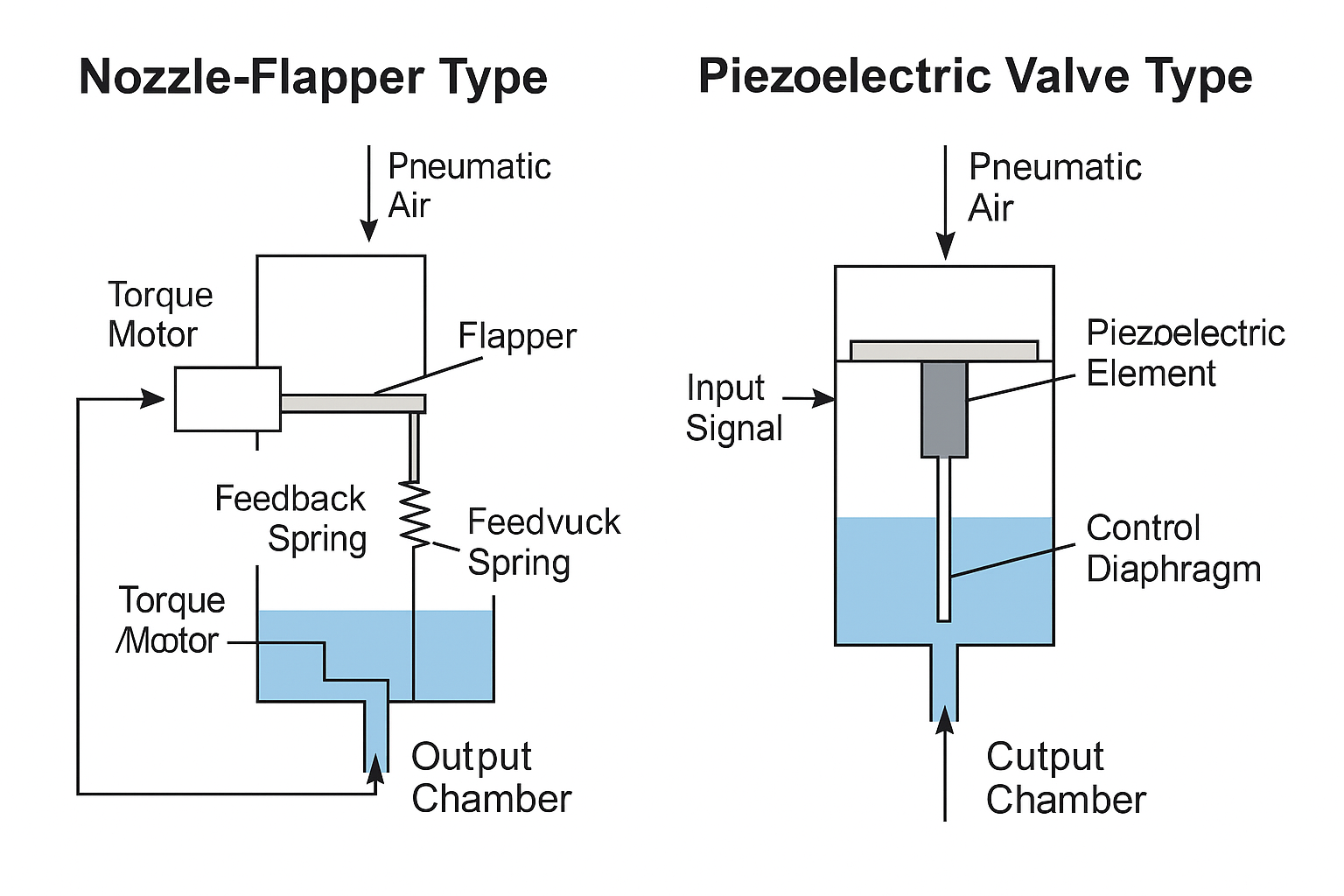
🔹 Nozzle-Flapper Type
This system operates on a force balance principle. It regulates backpressure by varying the distance between a nozzle and a flapper, which in turn controls the valve position. Key components include:
Fixed and variable orifices
Pneumatic chambers
A feedback spring
As the gap between the nozzle and flapper changes, the pressure on the diaphragm shifts, driving the actuator accordingly.
🔹 Piezoelectric Valve Type
This system uses the piezoelectric effect. When an electric signal is applied, a piezoelectric element deforms, adjusting airflow resistance and modulating output pressure.
Modern piezoelectric valves—such as the P9 and P20 series by Hoerbiger—are widely used in smart positioners.
A power-amplified piezoelectric valve integrates the piezoelectric controller with a pneumatic amplifier, enabling accurate control of valve actuators.
2. Air Consumption and Energy Efficiency
🔹 Nozzle-Flapper
Continuously consumes air, even at steady state.
Typically higher energy consumption.
Air loss occurs through the nozzle regardless of control activity.
🔹 Piezoelectric Valve
Consumes air only when correcting a position deviation.
In standby, air usage is nearly zero.
Siemens SIPART PS2 consumes only 1/10 to 1/20 the air compared to conventional designs.
3. Accuracy and Response Speed
🔹 Nozzle-Flapper
Mechanical contact may cause wear, vibration sensitivity, and output instability.
Precision declines over time due to mechanical drift and environmental factors.
🔹 Piezoelectric Valve
Compact, frictionless structure.
Immune to vibration and thermal variation.
Faster response and higher accuracy due to microprocessor-based control.
4. Control Algorithms
🔹 Nozzle-Flapper
Typically uses traditional PID algorithms.
Fast dynamic response but may suffer from nonlinearity and hysteresis.
🔹 Piezoelectric Valve
Supports advanced adaptive algorithms (e.g., single-neuron adaptive PSD control).
Better suited for complex, time-varying, or nonlinear systems.
5. Application Scenarios
🔹 Nozzle-Flapper
Suitable for cost-sensitive, low-precision applications.
Performs well in poor air quality environments due to rugged mechanical design.
Ideal for general-purpose control systems.
🔹 Piezoelectric Valve
Best suited for precision control, high-speed response, and low-energy applications.
Widely used in petrochemical, power generation, and high-end automation.
Requires clean and stable air supply.
Conclusion
Both nozzle-flapper and piezoelectric smart positioners have their own strengths and weaknesses:
| Feature | Nozzle-Flapper Type | Piezoelectric Valve Type |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Mechanical, simple | Compact, advanced |
| Air Consumption | Continuous | On-demand |
| Response Speed | Moderate | Fast |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Suitability | General environments | Demanding precision applications |
Selection should be based on application needs, including control precision, energy consumption, cost, and air quality conditions. As industrial automation moves toward smarter and more energy-efficient systems, piezoelectric valve positioners are increasingly favored in modern facilities.
