Solenoid valves are widely used in automation systems to control the flow of fluids or gases. Over time or during troubleshooting, it becomes necessary to test whether a solenoid valve is working correctly. This article outlines key components, step-by-step inspection methods, and safety tips for accurately diagnosing solenoid valve performance.
1. Main Components to Inspect
A solenoid valve’s performance primarily depends on two components:
The coil – generates electromagnetic force to move the valve plunger
The valve body – includes the plunger, seals, and ports that control fluid/gas flow
To determine whether a solenoid valve is in good condition, both components must be inspected.
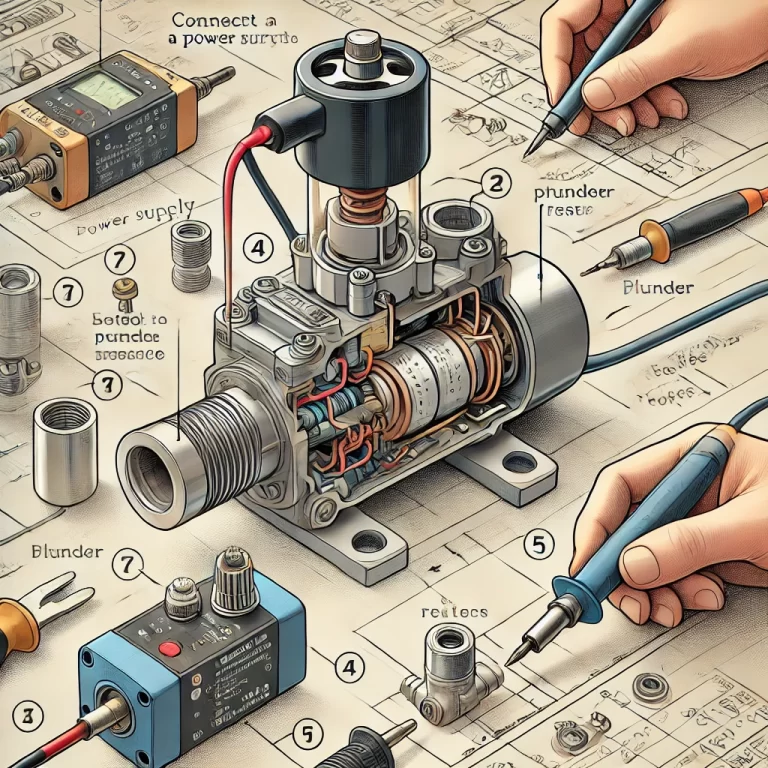
2. Methods to Test a Solenoid Valve
2.1 Power-On Functionality Check
Prepare a 24V DC power source (or the appropriate rated voltage for your coil).
Connect the power supply to the solenoid coil terminals.
Listen carefully: a distinct clicking sound indicates that the coil is generating a magnetic field and the plunger is actuating.
No sound may indicate coil burnout or mechanical blockage.
2.2 Coil Resistance Check (Using a Multimeter)
Disconnect power before testing.
Set the multimeter to resistance (Ω) mode.
Measure the resistance across the coil terminals:
A healthy coil typically reads a few tens of ohms (e.g., 20–50 Ω for 24V DC).
Very high or infinite resistance indicates an open coil (burnout).
Zero resistance may indicate a short circuit.
2.3 Magnetic Field Test
With power applied to the coil, bring a thin steel wire or small screwdriver close to the coil.
If magnetic attraction is detected, it confirms the electromagnetic field is present.
2.4 Plunger Movement Test
With power cycled ON and OFF, gently insert a small Allen wrench or tool into the valve’s plunger guide hole (if accessible).
Observe whether the plunger moves in when energized and returns when de-energized.
Lack of movement may indicate internal jamming or a damaged spring.
2.5 Flow and Leak Test (With Working Medium)
Connect the valve to its normal operating pressure using air or liquid within the valve’s rated pressure range.
Supply power to the coil.
Observe whether the valve successfully switches from open to closed or vice versa.
Check for leaks at the inlet, outlet, and around the valve body.
If a gas source is not available, you may apply light air pressure manually and plug the outlet, then blow through the inlet to simulate a leak test.
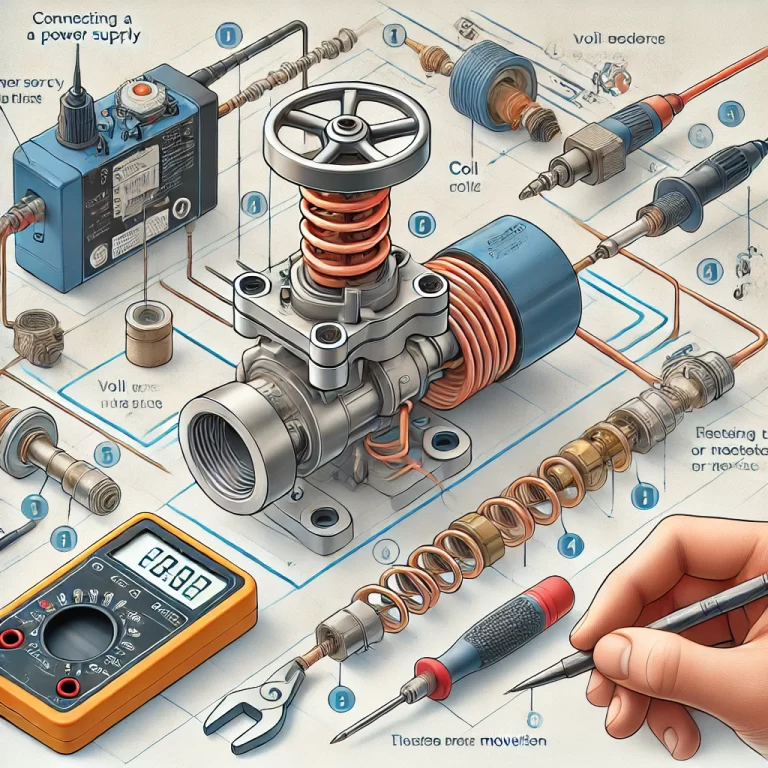
3. Precautions and Best Practices
Always confirm that the voltage and current ratings match the coil specifications.
Do not touch the diaphragm or internal seals with bare hands or sharp tools to avoid damage.
Use personal protective equipment when working with pressurized systems.
If the coil gets abnormally hot or fails repeatedly, check for incorrect voltage, poor wiring, or overuse beyond duty cycle.
4. Conclusion
By following the procedures above, you can effectively determine if a solenoid valve is operational or faulty. Accurate diagnosis not only prevents unnecessary replacements but also ensures the safe and reliable operation of fluid control systems.
