Bimetal thermometers are widely used in various industries due to their simple design, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. They play a crucial role in accurately measuring temperature in industrial, chemical, and even residential applications. However, improper use or exposure to adverse conditions can lead to their damage or failure. Understanding the causes of such damage is essential for proper maintenance and prevention. Below, we discuss the main factors contributing to bimetal thermometer damage and offer suggestions on how to address them.
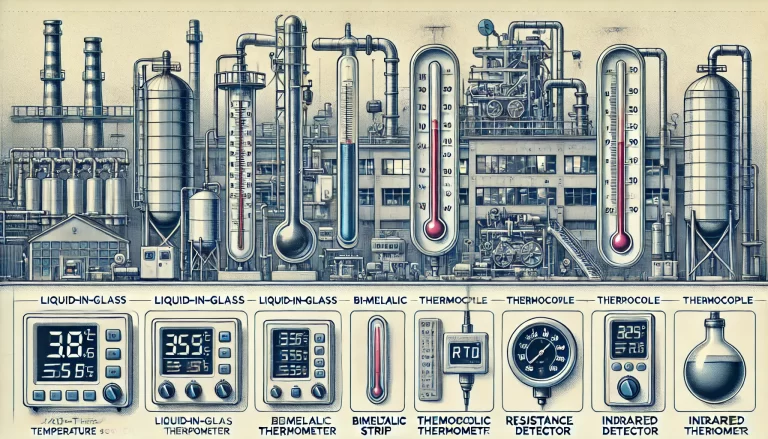
1. High-Temperature or Low-Temperature Overload
Bimetal thermometers are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges. Exposure to temperatures beyond these limits—whether excessively high or low—can cause permanent deformation of the bimetallic strip, leading to inaccurate readings or complete failure of the thermometer.
Prevention:
Always verify the thermometer’s operating range before use.
Use protective measures, such as temperature guards, when there is a risk of extreme temperatures.
Consider installing temperature limiters or alarms in systems where sudden temperature spikes are possible.
2. Mechanical Damage
The external structure of bimetal thermometers is susceptible to damage from physical impacts, vibrations, or mishandling. Mechanical damage can bend or break the bimetallic strip, making the thermometer unusable.
Prevention:
Avoid dropping or subjecting the thermometer to strong vibrations.
Install the thermometer in secure locations away from high-traffic areas or potential mechanical hazards.
Use shock-resistant thermometer models for environments prone to vibrations.
3. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
In environments with strong electromagnetic fields or radiation, the operation of bimetal thermometers may be compromised. This interference can distort the readings or cause the device to fail.
Prevention:
Use thermometers specifically designed for electromagnetic compatibility in high-EMI environments.
Ensure proper grounding of equipment and shielding of thermometer components.
Keep the thermometer away from high-frequency equipment such as radio transmitters or industrial microwaves.
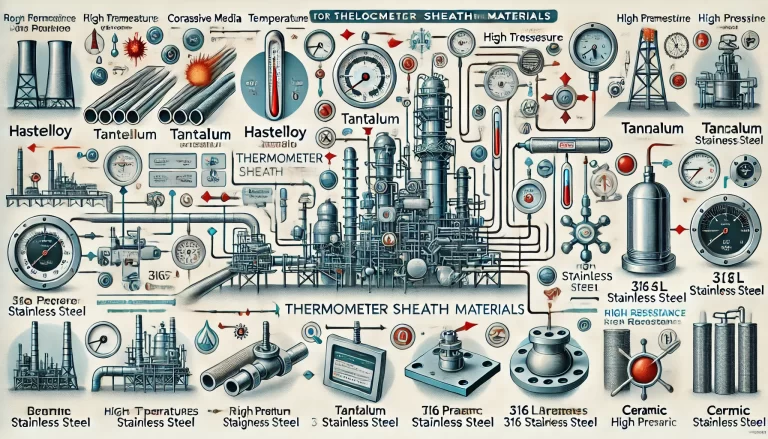
4. Corrosion from Liquids or Gases
Bimetal thermometers used in corrosive environments, such as chemical plants or areas with acidic gases, are prone to deterioration. The external casing or the internal bimetallic strip can suffer from chemical corrosion, leading to malfunction.
Prevention:
Select thermometers made with corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or Teflon-coated casings, for harsh environments.
Regularly inspect and clean the thermometer to remove corrosive residues.
Use protective enclosures or isolation diaphragms to shield the thermometer from direct contact with corrosive media.
5. Prolonged Usage and Material Fatigue
Over time, the materials used in bimetal thermometers may experience fatigue due to repeated thermal cycling or prolonged exposure to heat. This wear and tear can cause gradual loss of accuracy or outright failure.
Prevention:
Replace thermometers periodically based on the manufacturer’s recommendations or after a specified number of operating cycles.
Perform regular calibration checks to ensure accuracy.
For high-stress applications, consider using thermometers with reinforced or high-durability components.
Summary
Understanding the factors that can lead to bimetal thermometer damage—such as temperature overload, mechanical impacts, electromagnetic interference, corrosive environments, and material fatigue—is key to their effective maintenance and longevity. By taking preventive measures, such as choosing the right thermometer for the application, protecting it from harsh conditions, and adhering to proper maintenance practices, you can ensure reliable and long-term operation.
Taking proactive steps to protect your bimetal thermometer will not only enhance its lifespan but also ensure accurate and consistent performance, saving both time and costs associated with equipment failure.
