Introduction
Pt100 temperature sensors are widely used in industrial applications due to their accuracy and reliability. However, various issues can lead to measurement abnormalities, which may cause significant operational challenges. This article provides a detailed analysis of the common causes of Pt100 measurement issues, practical solutions, and key precautions to ensure accurate and consistent temperature monitoring.
Part 1: Common Causes of Abnormal Temperature Measurement
1. Loose Wiring Connections
In industrial environments, Pt100 sensors are often exposed to harsh conditions, such as vibration and temperature fluctuations. Over time, these factors can loosen wiring connections, leading to increased resistance in the measurement loop. This often results in temperature fluctuations or spikes. On trend graphs, such abnormalities may appear as irregular and spiky readings.
2. Oxidized Wiring Connections
High-temperature and high-humidity environments can accelerate the oxidation of wiring connections. Over time, oxidation can increase the resistance in the measurement circuit, causing measurement deviations. In severe cases, terminal screws may corrode, leading to poor connections or complete disconnection.
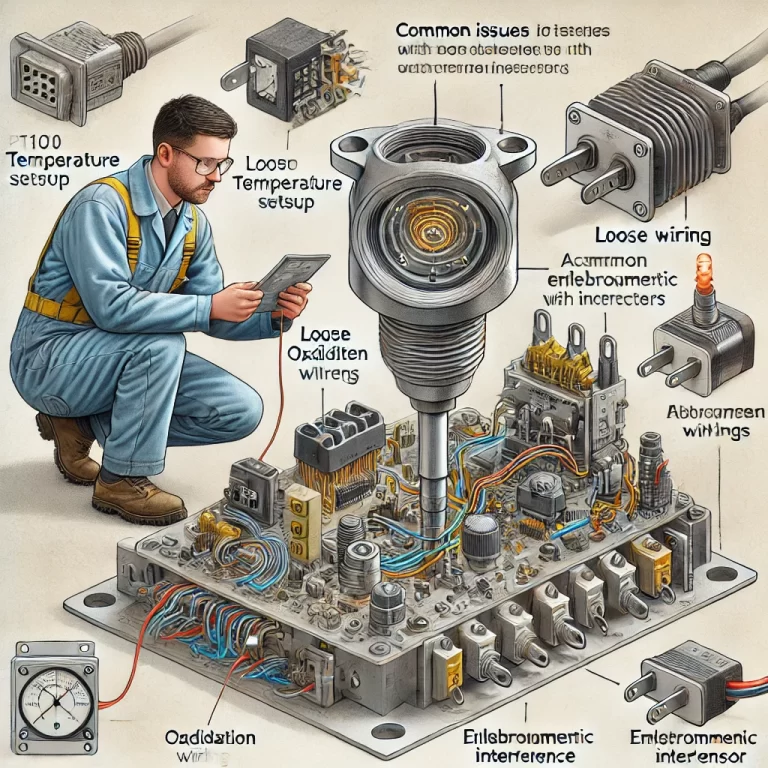
3. Induced Voltage in the Measurement Circuit
External voltage interference may occur in the measurement loop due to electromagnetic interference or improper grounding. This results in erroneous temperature readings, with the temperature appearing higher than the actual value. The magnitude of the error varies depending on the level of interference.
4. Abnormal Sampling Voltage at Terminal Boards
The sampling voltage at the Pt100 terminal boards should typically be 15V DC. Deviations from this value, whether higher or lower, can cause inaccuracies in temperature measurement. This issue is often related to hardware faults in the terminal boards.
5. Damaged Temperature Elements
A damaged Pt100 sensor often results in open-circuit or abnormally high resistance values. This issue is easily identifiable as the system (e.g., DCS) will typically display an error or “bad point” alert. For a functioning Pt100 sensor, the resistance at room temperature is approximately 110 Ω. Resistance deviations significantly beyond this range indicate damage.
6. Worn or Improperly Sealed Protective Tubes
In systems operating under negative pressure, such as certain pulverized coal systems, the protective tubes of Pt100 sensors may wear out due to prolonged exposure to abrasive materials. Once worn, external air may be drawn into the protective tube, cooling the sensor and causing lower-than-actual temperature readings. Poor sealing exacerbates this issue.

Part 2: Solutions to Address and Prevent Abnormal Measurement
1. Tighten Loose Connections
Inspect and tighten all connections in the measurement circuit. Ensure the use of washers or spring washers to secure the connections and minimize the likelihood of loosening over time. This simple step significantly improves measurement reliability.
2. Address Oxidized Connections
Remove oxidized sections of wiring or trim the oxidized ends. Strip the wires to expose fresh conductors and re-secure them. If water accumulation is observed in the connection boxes or cables, drain the water and ensure proper sealing. Adding a drainage outlet to the lowest point of protective conduits can help prevent water buildup. Maintain a dry environment within the connection boxes to avoid future oxidation.
3. Mitigate Induced Voltage Issues
Temporarily disconnect the wiring and discharge the circuit to the ground. While this method resolves immediate issues, identifying and addressing the root cause of the interference (e.g., faulty grounding or external voltage sources) is essential for a permanent solution.
4. Replace Faulty Terminal Boards
If sampling voltage abnormalities occur, replace the terminal board. Attempting repairs on-site is not recommended, as this may lead to inconsistent performance and reduced reliability. Sending the board back to the manufacturer for repair may be an option in specific cases.
5. Replace Damaged Sensors
Damaged Pt100 sensors should be replaced, as repairs are generally impractical. Verify the new sensor’s resistance and ensure that the measured value aligns with expected temperatures to confirm proper operation.
6. Repair or Replace Worn Protective Tubes
Inspect protective tubes regularly. If worn or punctured, replace or repair them by welding and sealing the damaged areas. Add sealing gaskets during reinstallation to improve the overall seal. To extend the lifespan of protective tubes, periodically rotate them to minimize wear on a single surface.
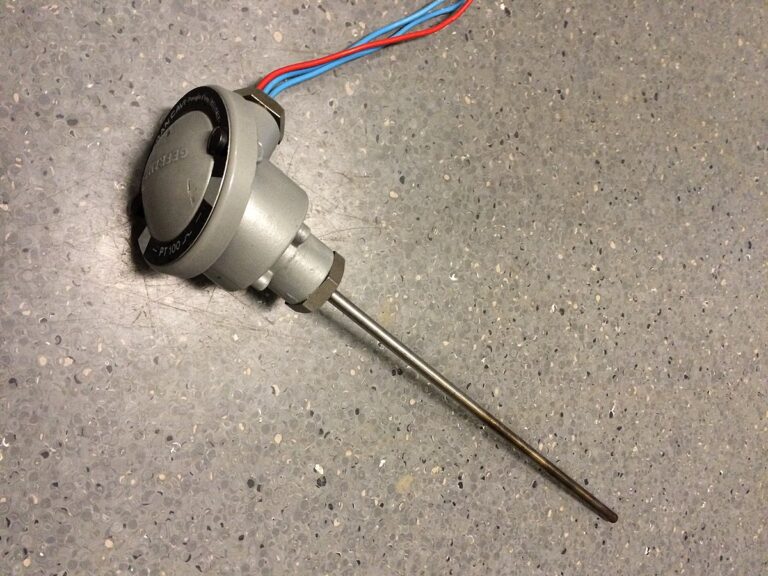

Part 3: Precautions During Abnormality Resolution
Verify Logic Dependencies: Before proceeding with repairs, check if the temperature measurement point is used in logic controls or safety protections. If so, disable the logic or protection functions temporarily and obtain the necessary approvals from operations personnel or plant management.
Communicate with Operators: Inform operators of any planned maintenance work, even if the affected measurement point is not part of a logic or safety system. Erroneous readings during maintenance may lead to incorrect assumptions or unnecessary interventions by operators.
Follow Approval Procedures: For critical systems, write a formal request for disabling safety protections. Proceed with maintenance only after receiving written approval.
Verify Post-Maintenance Performance: After resolving the issue, recheck the measurement system to ensure accurate and stable readings. Conduct a final review of all safety protections and logic systems to confirm normal operation.
Conclusion
Abnormalities in Pt100 temperature measurement systems can arise from various causes, including loose connections, oxidation, external voltage interference, and sensor damage. By systematically identifying and addressing these issues, operators can ensure reliable temperature monitoring and minimize operational disruptions. Regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for long-term system performance.
