Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are widely used in industrial applications due to their high accuracy, stability, and repeatability in temperature measurement. One critical component of an RTD is the extension section, which connects the sensing element to the external circuitry. Proper design and implementation of the extension section are essential to maintain the integrity and accuracy of the temperature measurement system. This article provides a detailed overview of the standards and best practices for designing RTD extension sections.
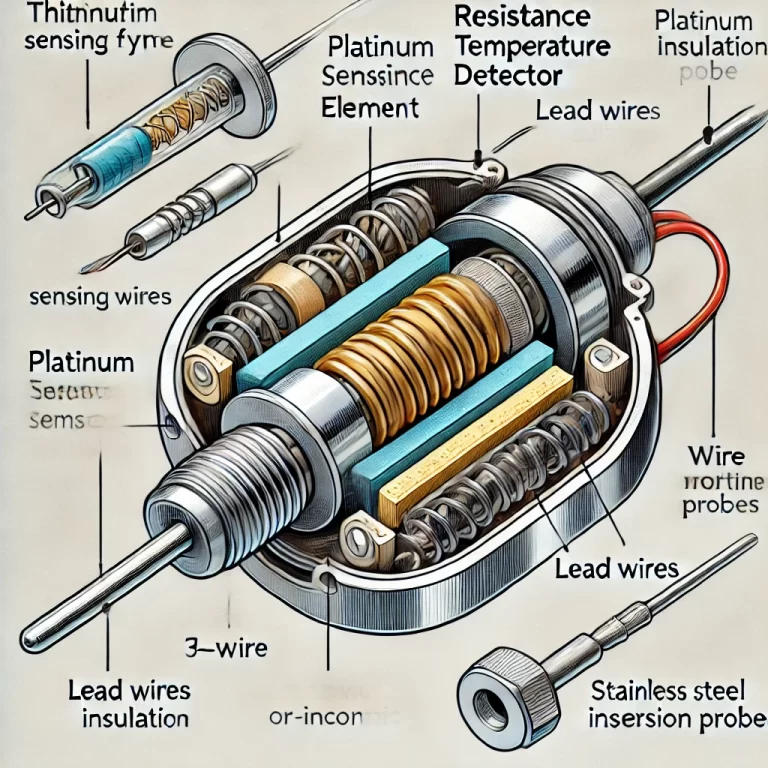
1. Relevant Standards and Guidelines
The design of RTD extension sections is primarily governed by international and national standards. Two key references are:
- IEC 60751:2008: This international standard specifies industrial platinum RTDs and provides technical requirements, including dimensional, electrical, and material specifications.
- GB/T 30121-2013: The Chinese equivalent of IEC 60751, this standard also includes additional requirements for localized applications in China.
These standards ensure uniformity in RTD performance and compatibility across different manufacturers and systems.

2. Key Design Considerations
Material Selection
The material used for the extension section plays a significant role in its performance and durability. Common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Offers excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it suitable for harsh industrial environments.
- Nickel or Nickel Alloys: Preferred in high-temperature or highly corrosive environments.
- Other Protective Coatings: In certain applications, materials may be coated with additional layers to enhance resistance to specific chemicals or environmental factors.
Mechanical Strength
The extension section must possess sufficient mechanical strength to withstand the following:
- Vibration and Shock: Industrial environments often expose RTDs to mechanical stresses.
- Installation Stress: Improper installation can deform or damage a poorly designed extension.
- Thermal Expansion and Contraction: The material should handle temperature variations without cracking or warping.
Heat Transfer Minimization
The extension section should minimize heat transfer from the process to the external environment, as this can lead to inaccurate readings. Factors to consider include:
- Length: A longer extension section reduces the effect of heat conduction but may require additional structural support.
- Thermal Conductivity: Low thermal conductivity materials are preferred to limit heat flow.
Electrical Insulation
Proper insulation is crucial to prevent electrical interference and maintain signal integrity. High-quality insulation materials, such as ceramics or specialized polymers, are commonly used.

3. Installation and Compatibility
The extension section must seamlessly integrate with other RTD components, such as:
- Protective Sheaths: Ensure that the extension is compatible with protective sheaths or thermowells, particularly in high-pressure or corrosive environments.
- Connection Boxes: The design should facilitate secure and straightforward connections to terminal blocks or transmitters.
4. Environmental Considerations
The extension section must meet the specific requirements of its application environment. For instance:
- Explosion-Proof Requirements: For hazardous environments, the extension section should meet explosion-proof standards, such as ATEX or IECEx.
- Waterproofing: For outdoor or submersed applications, ensure the extension section has appropriate sealing (e.g., IP68-rated designs).
5. Testing and Validation
To ensure reliability and compliance with standards, the extension section should undergo rigorous testing, including:
- Thermal Shock Tests: Evaluate the extension’s ability to handle sudden temperature changes.
- Corrosion Resistance Tests: Ensure the material’s longevity in aggressive environments.
- Mechanical Stress Tests: Confirm the structural integrity under real-world conditions.
Conclusion
The design of the extension section of an RTD is critical to the performance of the temperature measurement system. By adhering to established standards like IEC 60751 and GB/T 30121, selecting appropriate materials, and considering environmental factors, engineers can ensure that the extension section provides reliable and accurate temperature data over its operational life. Careful attention to these details will enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of industrial processes that rely on precise temperature monitoring.
