In the realm of industrial automation, the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) has long been regarded as the “brain” of control systems. It excels in executing logical operations, sequential control, timing, counting, and arithmetic tasks. However, as industrial processes grow increasingly complex, a standalone PLC system often falls short of meeting modern manufacturing demands. Enter the supervisory control system, commonly referred to as the upper computer or SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition). This system not only centralizes the management of multiple PLCs but also provides advanced functions such as data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. Below, we explore the critical roles of supervisory systems in advancing industrial automation.
1. Data Integration and Centralized Management
A single PLC has limited capacity in terms of data processing and control. In large-scale manufacturing plants, numerous PLCs operate simultaneously across various production stages. Supervisory systems act as a hub, integrating data from these diverse PLCs into a centralized platform. This setup enables operators to monitor and manage the entire production process from a control room, optimizing workflows and significantly improving overall operational efficiency.
Example Application:
For instance, in an automotive assembly plant, supervisory systems collect real-time data from different PLCs overseeing welding, painting, and quality inspection. With a consolidated view of operations, plant managers can quickly identify bottlenecks and make data-driven adjustments to enhance productivity.
2. Enhanced Visualization for Monitoring and Control
While PLCs offer robust control capabilities, their user interfaces are often basic and lack advanced visualization tools. Supervisory systems bridge this gap by utilizing configuration software to create dynamic, intuitive graphical interfaces. These interfaces provide real-time visual representations of equipment status, process parameters, and trends, enabling operators to monitor and control processes more effectively.
Example Application:
Consider an automated food processing line. A supervisory system’s graphical interface can display live data such as temperature, pressure, and production speed. Operators can make precise adjustments with a simple click, ensuring that products meet stringent quality standards.
3. Advanced Data Analysis and Decision Support
PLCs are designed for immediate control tasks, but their capacity for storing and analyzing historical data is limited. Supervisory systems excel in this area, capturing large volumes of data from PLCs and applying advanced analytics to uncover patterns and predict issues. This analytical capability provides critical insights that support informed decision-making.
Example Application:
In a chemical manufacturing plant, supervisory systems analyze historical temperature and pressure data to predict equipment failures. By implementing predictive maintenance strategies, the plant reduces unplanned downtime and maintenance costs, significantly boosting operational efficiency.

4. System Expansion and Network Integration
Traditional PLCs often operate within isolated systems, with proprietary communication protocols limiting interoperability. Supervisory systems overcome these limitations by integrating PLCs from various manufacturers into a unified network. They also facilitate the connection of smart devices such as sensors, robots, and IoT devices, paving the way for intelligent factories.
Example Application:
In a smart factory, supervisory systems seamlessly integrate data from PLCs, smart sensors, and robotic arms. This interconnected system enables real-time monitoring and control, supporting flexible and customized production processes that meet specific customer demands.

5. Driving the Future: Toward Intelligent Automation
As industrial automation transitions toward smart and networked systems, the integration of PLCs and supervisory control systems becomes inevitable. Supervisory systems not only enhance the capabilities of PLCs but also enable advanced functionalities such as big data analysis and optimization. By leveraging these technologies, factories can predict equipment failures, schedule preventive maintenance, and minimize production downtime. Furthermore, the support for multiple communication protocols ensures smooth data exchange across diverse devices, laying the foundation for building truly intelligent factories.
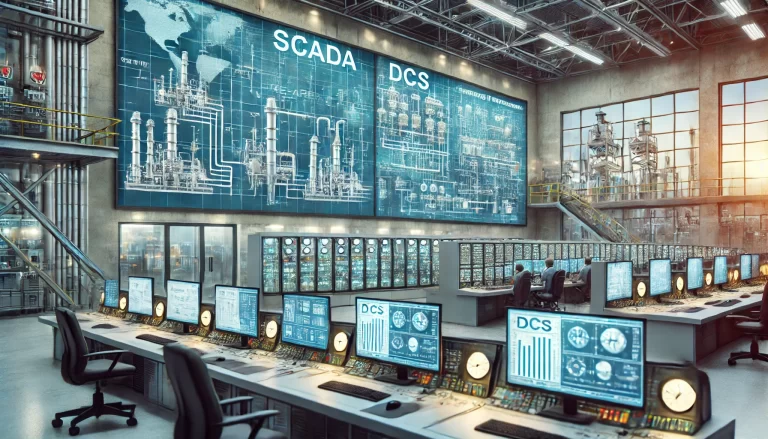
Conclusion and Outlook
The convergence of PLCs and supervisory systems represents a significant milestone in the evolution of industrial automation. While PLCs remain indispensable for real-time control, supervisory systems extend their functionality, offering centralized management, sophisticated analytics, and seamless integration. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as edge computing, artificial intelligence, and digital twins are poised to further revolutionize the relationship between PLCs and supervisory systems. By embracing these innovations, manufacturers can unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, flexibility, and intelligence in their operations.
