Radar level meters and magnetic sensitive electronic dual-color level meters are widely used instruments for liquid level measurement.
Some users may not be familiar with the differences between these two instruments. This article introduces their differences, advantages and disadvantages, and applicable scenarios, providing reference for engineers and technical personnel in instrument selection.
Radar Level Meter: Radar level meters utilize electromagnetic waves for non-contact measurement. By emitting and receiving reflected microwave pulses, they calculate the liquid level distance based on the time delay. This time-of-flight-based method allows them to adapt to high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments. They are also unaffected by changes in medium density or color.
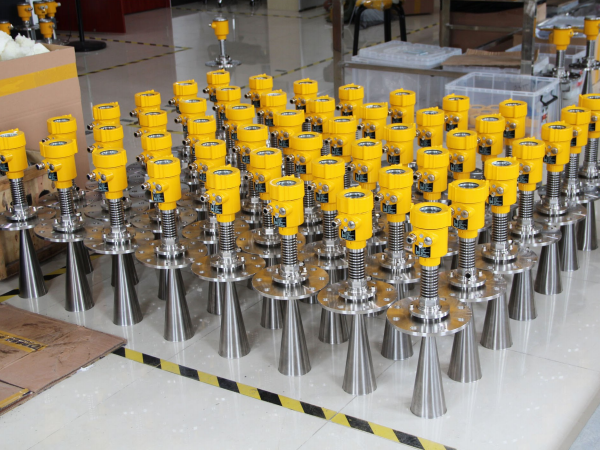

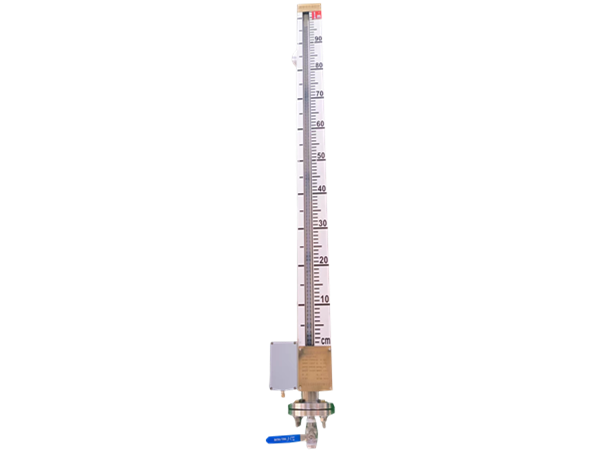
Magnetic Sensitive Electronic Dual-color Level Meter: This is a visual detection device combining a magnetic float and LED display technology. The core principle involves a magnetic float that rises and falls with the liquid level, driving an external flip indicator. At the same time, built-in LED lights change color according to the liquid level, providing a clear visual indication of the liquid state. This method, relying on physical displacement, is better suited for measuring clear, non-foamy, and non-viscous liquids.
Application Comparison:
- Radar level meters are widely used in industries such as chemical processing, petroleum, and food processing, especially in challenging environments, due to their non-invasive measurement method that reduces maintenance costs and the risk of contamination. However, for low-dielectric constant liquids, radar wave reflection weakens, potentially affecting measurement accuracy.
- Magnetic sensitive electronic dual-color level meters are more suitable for measuring clear liquids like water and oil and are commonly used in applications such as water treatment and petroleum storage tank monitoring. Their intuitive display makes it easy to quickly read data on-site. However, in environments with foam, suspended particles, or high-viscosity liquids, their accuracy decreases significantly. Additionally, physical contact over time can lead to wear and corrosion.

Technical and Economic Factors: Radar level meters, with their advanced signal processing and algorithm optimization, can achieve millimeter-level measurement accuracy and are unaffected by temperature or pressure changes, offering high stability. However, they are relatively expensive with higher initial investment costs. Magnetic sensitive electronic dual-color level meters, although less accurate, are generally sufficient for most industrial applications.
Their primary advantage lies in their intuitive display and affordability, making them suitable for budget-conscious scenarios with less stringent precision requirements. However, their mechanical components can increase the likelihood of malfunctions and maintenance needs.

Conclusion: The choice between radar level meters and magnetic sensitive electronic dual-color level meters depends on several factors, including the properties of the measured medium, measurement environment, budget, and precision and reliability requirements.
For high-precision measurements in complex conditions, radar level meters are undoubtedly the better choice, whereas in cost-sensitive and simple applications requiring quick visual readings, magnetic sensitive electronic dual-color level meters are more appropriate.
