Explosion-proof flexible conduits, also known as explosion-proof flexible metal hoses, play a crucial role in hazardous areas where flammable gases, vapors, or combustible dusts are present. These conduits are designed to protect electrical cables and maintain the integrity of explosion-proof enclosures. Proper installation is essential to ensure system safety, durability, and compliance with explosion-proof standards.
This article outlines the critical aspects to consider during installation and highlights common mistakes to avoid.
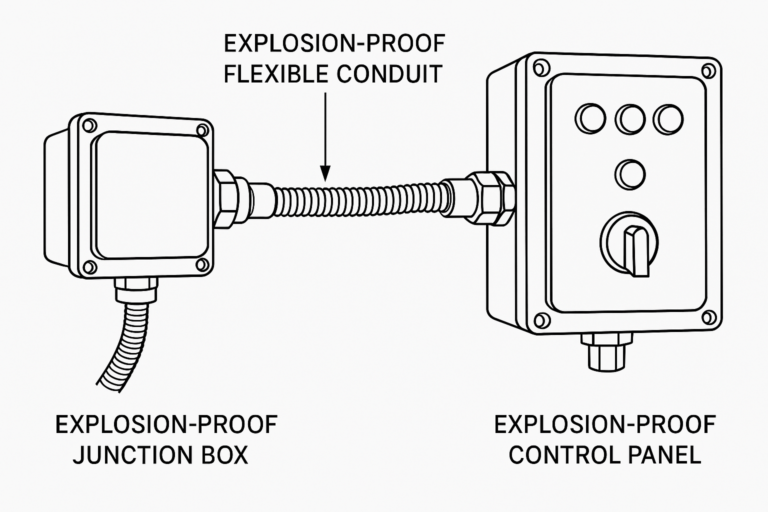
1. Proper Selection of Explosion-Proof Flexible Conduits
Before installation, ensure the selected flexible conduit meets all necessary requirements:
Explosion-proof certification: The conduit must be certified by recognized bodies such as ATEX, IECEx, UL, or CNEX, and meet the same hazardous area classification as the equipment it connects to.
Size compatibility: Confirm that the conduit diameter, thread type (e.g., NPT, G, M), and length are compatible with both terminal devices (e.g., control boxes, junction boxes).
Mechanical specifications: The conduit should resist corrosion, high temperatures, vibrations, and mechanical stress expected in the installation environment.
2. Secure End Connection and Thread Matching
Proper connection at both ends is crucial:
Ensure that the threaded connectors match the enclosures and junction boxes (both thread type and size).
Use locking nuts, sealing washers, or explosion-proof cable glands to secure connections and prevent gas ingress.
Avoid using unauthorized adapters or thread converters, which can compromise the flameproof integrity of the system.

3. Sealing and Ingress Protection
Sealing is critical for maintaining IP protection (typically IP65/IP66/IP67) and explosion-proof integrity:
Apply appropriate sealing gaskets or sealing compounds at junctions to ensure dustproof and waterproof protection.
Use compression fittings to achieve tight sealing between the conduit and the connected enclosure.
Verify that the sealing materials are chemical-resistant if used in corrosive environments (e.g., oil refineries, wastewater plants).
4. Routing and Mechanical Support
Correct routing of flexible conduits ensures safety and prevents mechanical stress:
Avoid tight bends—respect the minimum bending radius specified by the manufacturer to prevent wire damage or internal sheath stress.
Avoid placing weight on the conduit. If the conduit spans a long distance, use support clamps or brackets to relieve mechanical load on terminals.
Do not route conduits through hot zones, vibrating machinery, or areas exposed to corrosive chemicals unless adequately protected.

5. Electrical Grounding and Continuity
Explosion-proof flexible conduits with metallic braiding must be properly grounded:
Ensure electrical continuity between both ends of the conduit by using bonding conductors or grounding lugs.
Ground the flexible conduit to the same potential as the connected equipment, especially if shielding or EMC protection is required.
Test continuity after installation using a multimeter to verify resistance is below the acceptable limit (typically <1Ω).
6. Post-Installation Inspection and Testing
After installation:
Check all threads are fully engaged and tightened.
Inspect seals, gaskets, and any sealing compound used.
Confirm that no excessive strain or mechanical force is acting on the conduit.
Ensure conduit labels and certification marks are visible and intact for compliance inspection.

⚠️ Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Potential Risk |
|---|---|
| Using mismatched or non-explosion-proof connectors | Can breach the flame path and cause ignition |
| Failing to seal threads or conduit ends properly | Allows explosive gas or dust ingress |
| Over-bending or kinking the conduit | Causes internal damage or short circuits |
| Letting the conduit bear weight or hang unsupported | Can lead to mechanical failure or disconnection |
| Using uncertified or fake components | Fails inspection and creates safety hazards |

Conclusion
Explosion-proof flexible conduits are indispensable in hazardous industrial environments. However, their effectiveness depends heavily on correct installation and adherence to safety standards. Always select certified products, match threads and sizes precisely, ensure proper sealing and grounding, and avoid physical stress during routing. By following these best practices, you can ensure long-term reliability and safety of explosion-proof electrical systems.
