When measuring gas or steam flow with a vortex flowmeter, it is essential to measure the fluid pressure. Most manufacturers recommend placing the pressure measurement point downstream of the vortex sensor. However, some manufacturers suggest it can be placed upstream. So, which position is ideal for the pressure measurement point?
Why the Pressure Measurement Point Should Be Placed Downstream
The vortex flowmeter works on the principle that the frequency of vortex shedding is proportional to the average flow velocity downstream of the vortex generator. This means that the output frequency is an indication of the volume flow rate at that specific point.
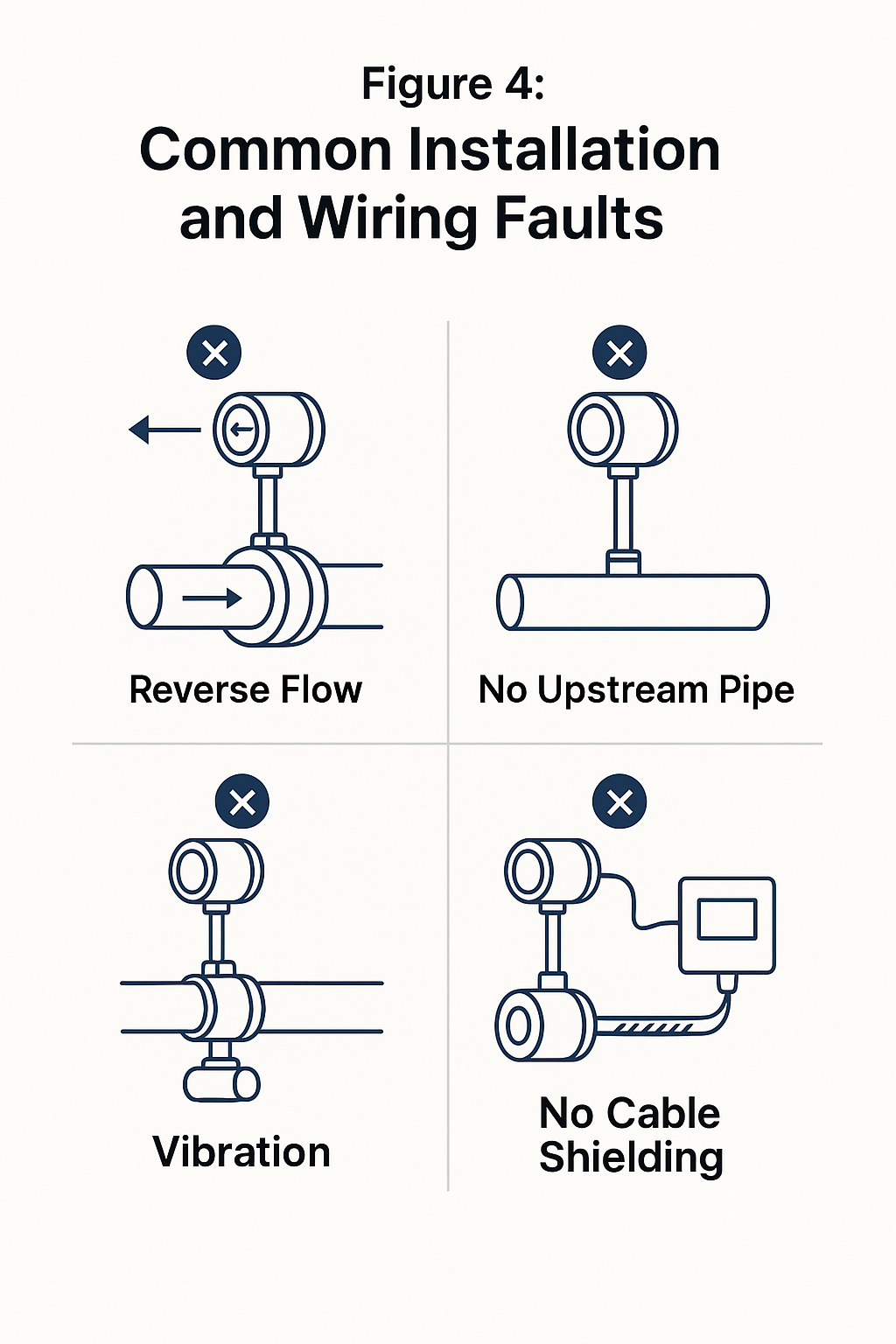
Pressure Measurement for Gas and Steam
For gas measurement, the volume flow must be converted to the standard volume flow, while for steam, the flow rate must be corrected for fluid density. In both cases, the pressure of the fluid under operating conditions is crucial to these calculations. As gases and steam are compressible fluids, the static pressure at different points along the pipeline varies, making the choice of pressure measurement location very important.
Theoretical Consideration for Downstream Measurement
Ideally, the pressure measurement point should be located at the downstream side of the vortex generator, where the flow velocity is directly related to the frequency of vortex shedding. However, most manufacturers do not provide pressure ports on the sensor body, so users must install the pressure measurement point downstream of the vortex flowmeter. The pressure measured at this location will be slightly higher than the actual pressure at the vortex shedding point, but for flowmeters with accuracy levels between 0.75% and 1.5%, the error introduced by this difference is negligible.

The Errors Introduced by Upstream Pressure Measurement
When the pressure measurement point is placed upstream of the vortex flowmeter, the measured pressure will be significantly higher. This is because the fluid experiences a pressure drop as it passes through the vortex shedding element. Yokogawa, a well-known manufacturer, provides a formula for the pressure drop in vortex flowmeters:
Where:
-
is the pressure drop (MPa)
-
is the fluid density (kg/m³)
-
is the flow velocity (m/s)
As shown in the formula, the pressure drop increases with flow velocity. For example, at a flow velocity of 60 m/s, the pressure drop becomes significant, and the upstream pressure can be up to 2% higher than the actual value, leading to an overestimation of the mass flow rate.
Example: Saturated Steam at 0.8 MPa
For saturated steam at 0.8 MPa, with a density of approximately 5.15 kg/m³, at a flow velocity of 60 m/s, the pressure drop Δp is 19.5 kPa. This results in an upstream pressure of 0.8195 MPa. With a density of 5.26 kg/m³, the mass flow calculation is 2% higher than it should be, which can cause significant errors.
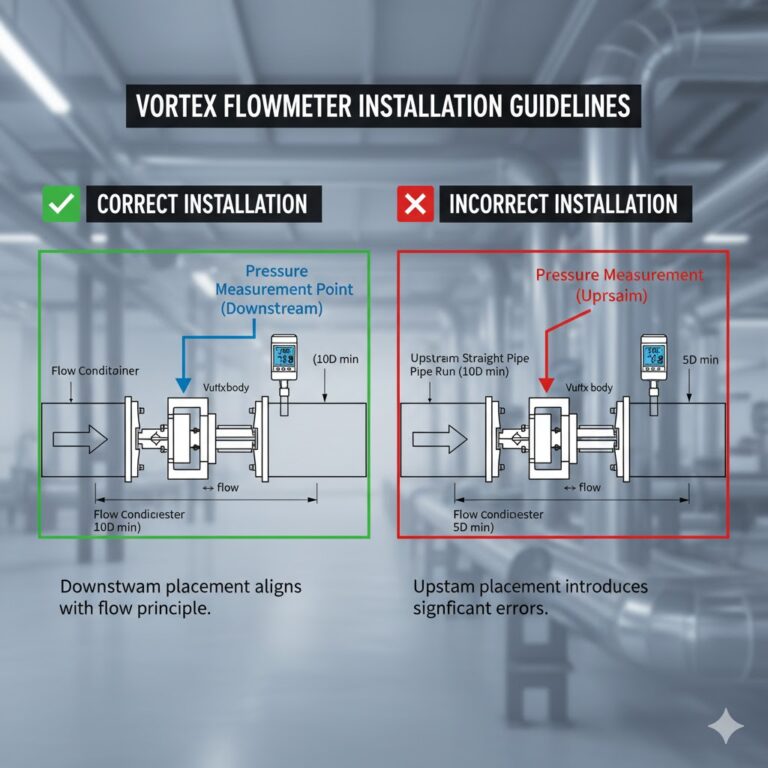
Opinions from Industry Standards
In the British Standard BS 7405-1991 “Guidelines for the Application and Selection of Flow Meters for Flow Measurement of Fluids in Closed Pipes,” the pressure measurement point is recommended to be placed downstream of the vortex flowmeter, which aligns with the vortex flowmeter’s working principle. Additionally, a typical vortex meter design includes a pressure port directly beneath the vortex detection element. This design ensures more accurate pressure measurement compared to placing the port downstream in the pipeline.
Conclusion
The correct placement of the pressure measurement point is crucial for accurate flow measurement with a vortex flowmeter. While the ideal position would be at the downstream side of the vortex generator, practical considerations often lead to placing it downstream in the pipeline. Placing the measurement point upstream can introduce significant errors, especially at higher flow velocities, leading to inaccurate flow calculations.
By following the proper installation guidelines, the accuracy of the vortex flowmeter can be maintained, ensuring reliable flow measurement for various applications, including gas and steam.
