1. Introduction
In cable installation, bending radius refers to the minimum radius a cable can be bent without causing mechanical or electrical damage. It is a critical factor in ensuring cable performance, longevity, and compliance with international standards. Ignoring bending radius requirements may lead to insulation cracks, conductor deformation, or signal degradation.
2. What Is Cable Bending Radius?
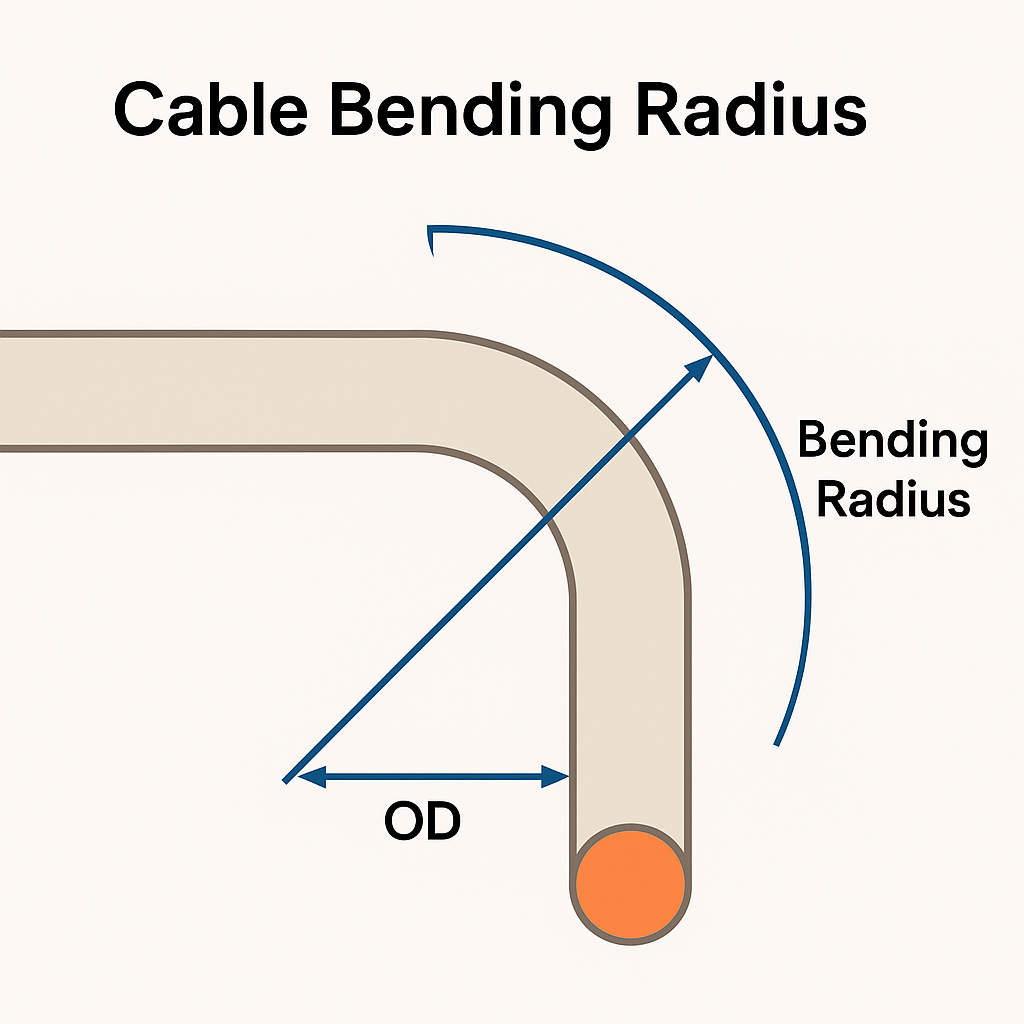
Definition: The bending radius is the minimum curvature a cable can safely achieve during installation or operation.
Notation: Often specified as a multiple of the cable’s outer diameter (OD), such as 10 × OD.
Types:
Dynamic bending radius: Applicable during pulling or moving.
Static bending radius: Applicable once the cable is installed and stationary.
3. International Standards & References
Different standards specify bending radius requirements based on cable type:
| Cable Type | Standard | Typical Minimum Bending Radius |
|---|---|---|
| Power Cable (XLPE insulated) | IEC 60502-1 | 12 × OD (during installation), 8 × OD (fixed) |
| Control Cable | IEC 60227 | 6–10 × OD |
| Fiber Optic Cable | IEC 60794 | 20 × OD (dynamic), 10 × OD (static) |
| Instrumentation Cable | IEEE 1185 | 8–12 × OD |
4. Why Bending Radius Matters
4.1 Mechanical Integrity
Over-bending can cause insulation cracks, jacket deformation, or shield damage.
Conductors may shift or break, leading to premature failure.
4.2 Electrical Performance
Impedance changes in communication cables may cause signal reflection.
Increased attenuation in fiber optic cables due to micro-bending losses.
4.3 Safety & Compliance
Excessive bending can compromise dielectric strength, leading to short circuits.
Non-compliance may violate IEC/IEEE installation requirements.
5. Calculation Example
If a power cable has an outer diameter of 50 mm and the standard specifies 12 × OD during installation:
Minimum Bending Radius = 12 × 50 mm = 600 mm
This means the cable must not be bent to a radius smaller than 600 mm during pulling.
6. Best Practices for Maintaining Bending Radius
Check Manufacturer’s Data Sheet
Always confirm specific bending radius values before installation.
Use Cable Rollers & Guides
Prevent sharp bends during pulling.
Maintain Radius in Cable Trays & Conduits
Avoid tight corners without proper support.
Training for Installation Teams
Ensure awareness of bending radius requirements.
Inspect After Installation
Verify no sections are over-bent, especially at terminations.

7. Conclusion
The bending radius is not just a number on a specification sheet—it is a vital installation parameter that protects the mechanical integrity, electrical performance, and service life of cables. Adhering to recommended bending radius values ensures safety, reliability, and compliance in electrical and instrumentation systems.
