Instrument technicians play a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of industrial systems by maintaining, installing, and troubleshooting various instruments. A well-structured weekly study plan can help both beginners and experienced technicians enhance their knowledge and skills systematically. Below is a detailed plan designed for self-study.
Monday: Fundamentals of Instrumentation
- Objective: Understand the basic concepts and principles of instrumentation.
- Study Topics:
- Measurement Principles:
- Pressure: Types (gauge, absolute, differential) and measurement methods (bourdon tube, diaphragm).
- Temperature: Devices like thermocouples, RTDs, and thermistors.
- Flow: Measurement techniques such as electromagnetic, ultrasonic, and orifice plates.
- Level: Applications of float-based, radar, and ultrasonic level measurement.
- Overview of Instrumentation Types:
- Sensors, transmitters, controllers, and indicators.
- Typical usage in industries like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
- Measurement Principles:
- Activities:
- Read introductory materials or watch tutorials.
- Identify and list different instruments in your workplace and their functions.

Tuesday: Electrical Fundamentals
- Objective: Develop a strong foundation in electrical concepts relevant to instrumentation.
- Study Topics:
- Basic Electrical Principles:
- Voltage, current, and resistance (Ohm’s Law).
- Understanding AC vs. DC circuits.
- Power calculations (P=VI).
- Circuit Components:
- Relays, switches, fuses, and contactors.
- Working with resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
- Tools and Measurements:
- Using a multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Understanding how to use tools like an ammeter and clamp meter.
- Basic Electrical Principles:
- Activities:
- Perform simple electrical measurements.
- Build a basic circuit using resistors and a battery.
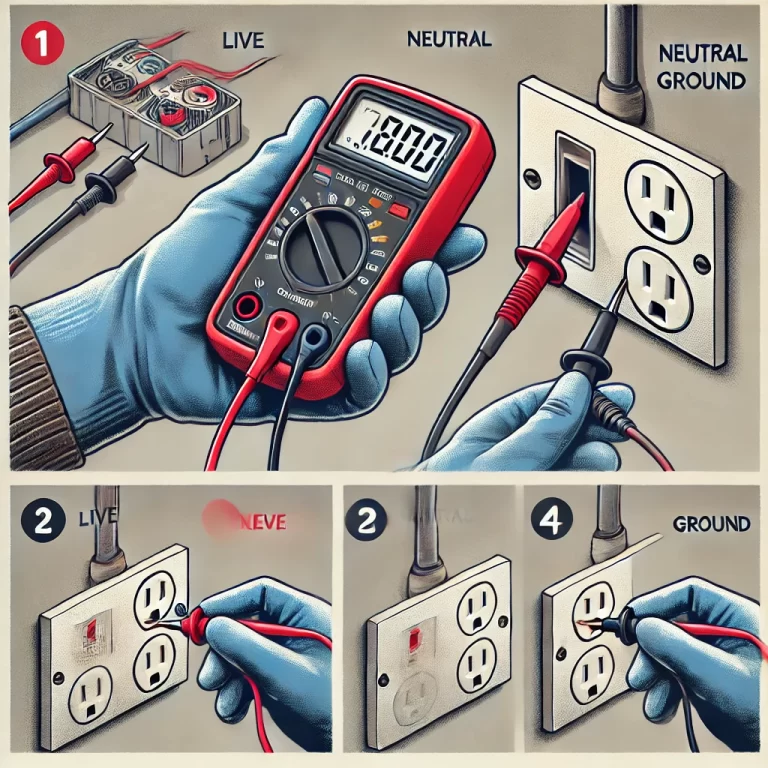
Wednesday: Instrument Installation and Maintenance
- Objective: Learn how to properly install, calibrate, and troubleshoot instruments.
- Study Topics:
- Installation Basics:
- Standard procedures for installing pressure and temperature transmitters.
- Pipe fittings, welding basics, and tubing layout.
- Calibration Techniques:
- Using a pressure calibrator or dead-weight tester.
- Calibrating a temperature transmitter with a dry block calibrator.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting:
- Common issues: signal drift, sensor failure, communication errors.
- How to perform preventive maintenance and diagnostic tests.
- Installation Basics:
- Activities:
- Practice installing a simple sensor on a test setup.
- Simulate troubleshooting common issues.

Thursday: Automation and PLC Basics
- Objective: Explore the integration of instruments into automated systems.
- Study Topics:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs):
- PLC architecture: inputs, outputs, CPU, and programming interface.
- Basics of ladder logic programming.
- Introduction to HMI (Human-Machine Interface) systems.
- Communication Protocols:
- Analog signals: 4-20mA, 0-10V.
- Digital communication: Modbus, Profibus, and Ethernet/IP.
- Signal conditioning and noise reduction.
- Control Loops:
- Open vs. closed-loop control systems.
- PID control basics.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs):
- Activities:
- Write a simple PLC program (e.g., start/stop a motor with a push button).
- Connect an instrument to a PLC and observe data acquisition.

Friday: Case Studies and Application
- Objective: Apply knowledge to real-world scenarios and analyze practical applications.
- Study Topics:
- Industrial Case Studies:
- Analyze specific examples such as flow measurement in a chemical plant or temperature control in food processing.
- Instrument Selection:
- Criteria for selecting the right instruments based on application.
- Factors like accuracy, range, and environmental conditions.
- Layout Design:
- Drawing a simple instrument loop diagram (ILD).
- Understanding Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID).
- Industrial Case Studies:
- Activities:
- Study an industrial process flowchart and identify key instruments.
- Design a basic instrument setup for a given scenario.

Saturday: Safety and Standards
- Objective: Gain knowledge about safety practices and industry standards.
- Study Topics:
- Electrical Safety:
- Lockout-tagout (LOTO) procedures.
- Insulation testing and earthing requirements.
- Explosion-Proof Instruments:
- Intrinsically safe designs for hazardous environments.
- ATEX and IECEx certifications.
- Industry Standards:
- ANSI/ISA standards for instrument installations.
- Calibration and maintenance documentation.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Importance of PPE and its correct usage.
- Electrical Safety:
- Activities:
- Conduct a safety inspection of your work area.
- Familiarize yourself with safety regulations specific to your region.

Sunday: Review and Hands-On Practice
- Objective: Consolidate the week’s learning through review and practice.
- Activities:
- Review Notes:
- Revisit key concepts and notes from the week.
- Identify areas requiring more attention.
- Skill Testing:
- Practice installing, calibrating, or troubleshooting an instrument.
- Complete sample quizzes or certification-style questions.
- Plan Ahead:
- Set goals for the next week.
- Research additional resources like books or online courses.
- Review Notes:

Tips for Success:
- Use Reliable Resources:
- Books: Instrument Engineers’ Handbook by Béla G. Lipták, Process Control Instrumentation Technology by Curtis D. Johnson.
- Online courses from platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or LinkedIn Learning.
- Focus on Practice:
- Allocate at least 40% of your time to hands-on work. Theory without practice will not yield strong results.
- Track Your Progress:
- Maintain a log of the topics covered and practical tasks completed.
- Regularly evaluate your improvement through tests or real-world application.
By following this weekly plan consistently, you will build a strong foundation in instrumentation and automation, preparing you for complex tasks and career advancement in the field.
