Abstract
Gas leak detectors are critical instruments for ensuring workplace safety, preventing environmental pollution, and protecting human health. However, their accuracy degrades over time due to sensor aging, environmental conditions, or frequent use. Regular calibration is not just a maintenance task—it is a rigorous metrological activity that ensures measurement traceability and reliability. This article explains the importance of calibration, outlines standard verification methods, highlights potential risks of neglect, and provides recommendations for best practices.
1. Introduction
Gas leaks pose significant risks in industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas, fire safety, and refrigeration. Undetected leaks can lead to explosions, poisoning, or environmental hazards. Gas leak detectors act as the first line of defense; however, their performance depends on accurate measurement and reliable alarm thresholds. Without regular calibration, detectors may drift, resulting in either false alarms or missed detections.
2. Why Calibration Matters
Calibration ensures that the detector’s readings are traceable to national or international standards. The key purposes include:
Traceability: Aligning measurement results with higher-level standards.
Accuracy: Verifying alarm thresholds and concentration readings.
Reliability: Ensuring stable operation in real-world environments.
Compliance: Meeting safety regulations (e.g., ISO, IEC, JJG 693-2011 in China).
👉 Neglecting calibration may lead to catastrophic safety incidents or unnecessary production downtime.
3. Standard Calibration Procedures
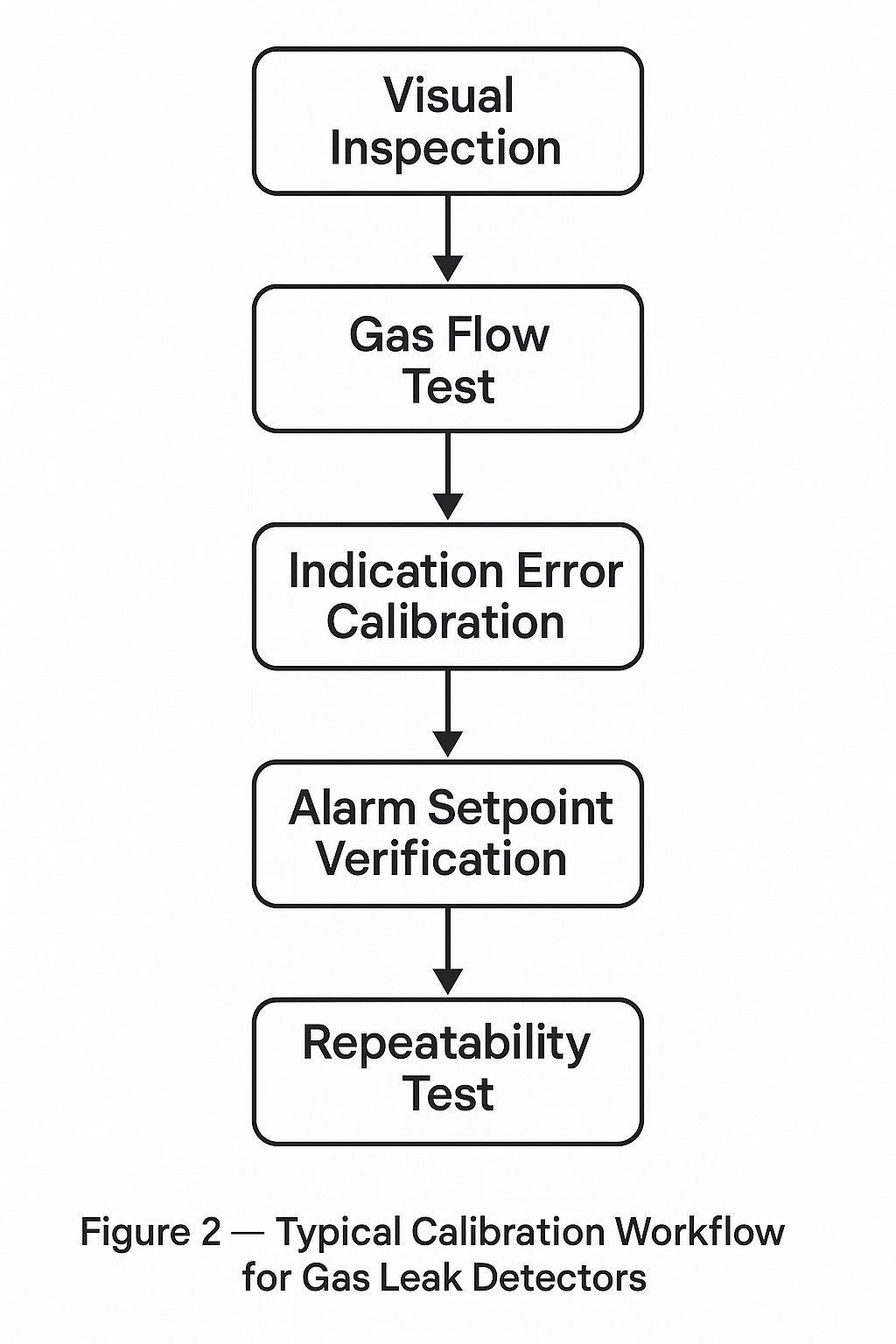
A complete calibration and verification process typically involves:
Visual Inspection: Check housing, display, power supply, and sensor condition.
Gas Flow Test: Introduce standard gas to confirm response.
Indication Error Calibration: Compare displayed value with reference concentration.
Alarm Setpoint Verification: Adjust thresholds to ensure correct triggering.
Repeatability Test: Confirm stable readings across multiple trials.
Adjustment & Documentation: Correct sensitivity, zero-point drift, and issue a calibration certificate.
Calibration should be performed in a controlled environment (constant temperature and humidity) using certified standard gases.
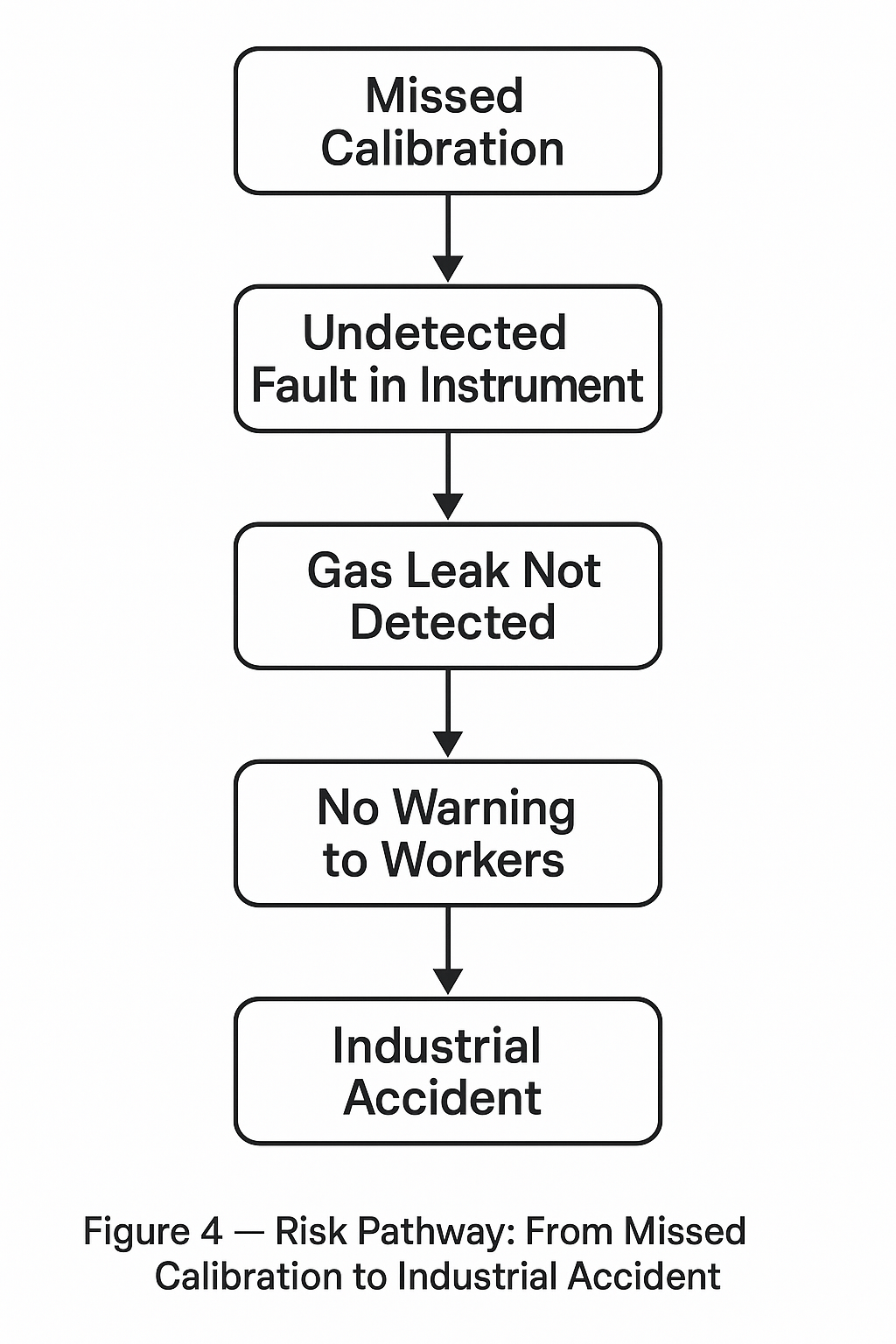
4. Risks of Neglecting Calibration
Failing to conduct periodic calibration can result in:
Missed Leaks: Low sensitivity may cause the detector to overlook dangerous leaks.
False Alarms: Excessive sensitivity drift can trigger unnecessary shutdowns.
Legal & Compliance Risks: Violating occupational health and safety regulations.
Economic Loss: Production downtime and increased maintenance costs.
Case Example: In a chemical plant, a detector that had not been calibrated for two years failed to detect a methane leak, leading to a fire incident and millions in damages.
5. Recommended Calibration Intervals
Routine Use: Every 6–12 months depending on manufacturer recommendations.
High-Risk Environments: Every 3–6 months.
After Major Maintenance or Sensor Replacement: Immediate recalibration.
Pre-commissioning: Before installation into safety-critical processes.
6. International Standards and Guidelines
Gas leak detector calibration is governed by multiple international and national standards:
ISO/IEC 17025: General requirements for calibration laboratories.
JJG 693-2011 (China): Verification regulation for combustible gas detectors.
EN 45544 (EU): Workplace gas detection standards.
OSHA & ANSI Standards (USA): Workplace safety compliance.
These standards ensure calibration is traceable, repeatable, and legally valid.
7. Conclusion
Calibration is not simply an adjustment—it is a structured quality assurance activity that integrates gas leak detectors into a unified measurement traceability system. By following proper calibration methods, companies can:
Improve worker and environmental safety.
Reduce false alarms and unnecessary shutdowns.
Meet regulatory compliance requirements.
Enhance confidence in safety-critical monitoring.
👉 Regular calibration is the most responsible investment for ensuring safety in hazardous industries.
