Abstract
In Modbus communication systems based on RS-485, termination resistors are often mentioned as a means of improving signal integrity. However, whether they are always required depends on several technical factors such as cable length, baud rate, and network topology. This document explains the principles, application scenarios, and practical guidelines for deciding when to use termination resistors.
1. Role of Termination Resistors
Termination resistors are used to match the characteristic impedance of RS-485 communication lines, typically around 120 Ω.
When a signal travels along the cable and reaches an unmatched end, part of the signal is reflected back.
These reflections can cause distortion, noise, or CRC errors in Modbus data frames.
By installing a resistor at each end of the bus, reflections are absorbed, ensuring stable and reliable communication.
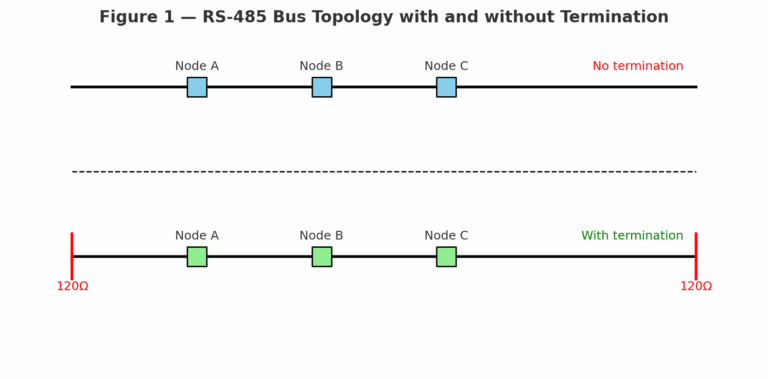
2. When Termination Is Not Always Necessary
Although termination is important in theory, in practice not all Modbus networks require it. Several factors influence this decision:
Communication Distance:
Short networks (< 50 m) usually show negligible reflection.
Baud Rate:
At low baud rates (e.g., 9600 bps), signals propagate slowly relative to cable delay, reducing reflection effects.
Number of Devices:
Fewer nodes mean simpler signal paths and fewer opportunities for interference.
Cable Quality:
High-quality, RS-485-compliant shielded cables maintain stable impedance, lowering the risk of reflection.
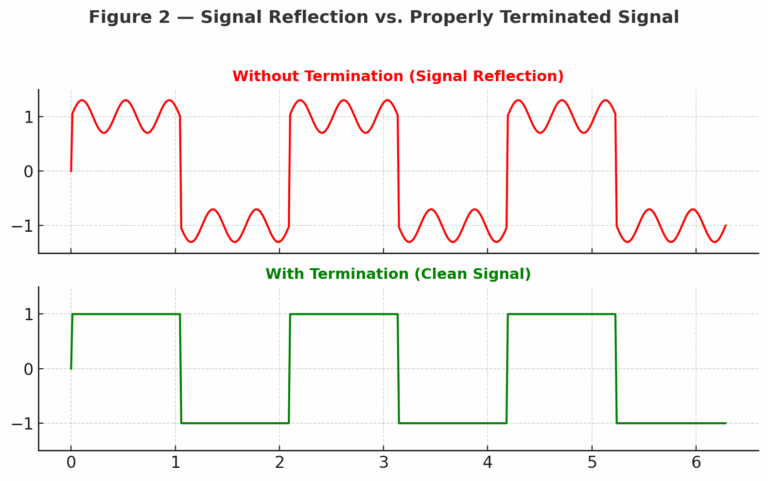
3. Potential Challenges of Termination
While beneficial, termination resistors may also introduce issues:
Excessive Attenuation: Too many connectors, stubs, or branches combined with termination can weaken the signal.
Incorrect Resistor Value: Standard RS-485 uses 120 Ω. Using inappropriate values may increase current draw or damage transceivers.
Power Consumption: Each termination resistor draws additional current, which can stress low-power systems.
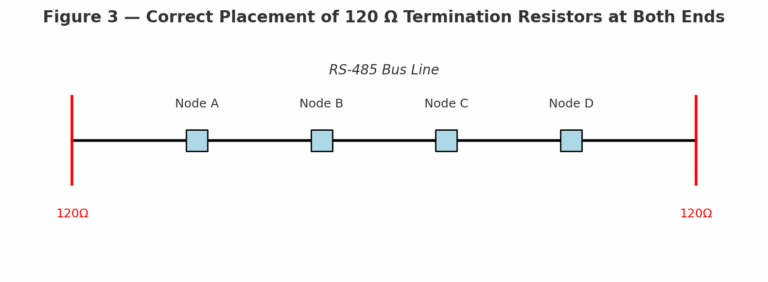
4. Practical Guidelines to Decide
To determine whether termination resistors are required, consider the following steps:
Check Network Length
100 m: Termination strongly recommended.
Measure Signal Quality
Use an oscilloscope: reflections or distorted edges indicate the need for termination.
Gradual Optimization
Adjust baud rate, cable routing, and device placement before finalizing resistor installation.
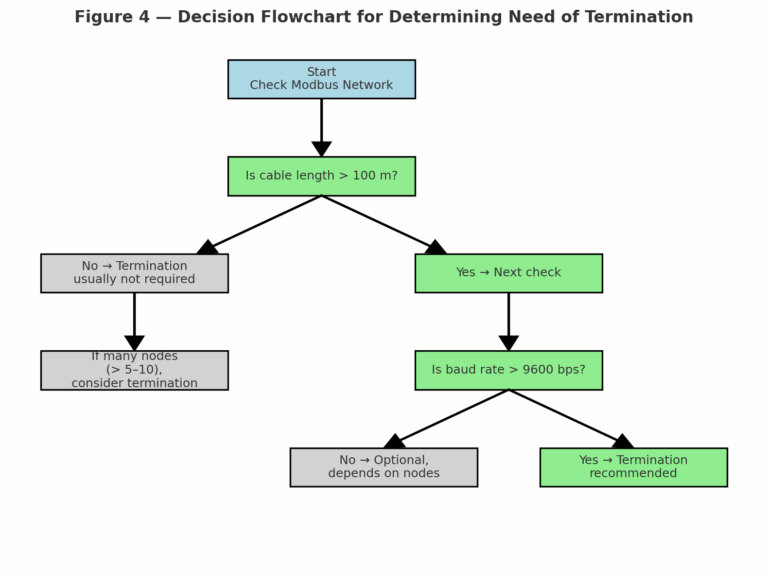
5. Recommended Decision Table
| Distance | Baud Rate | Node Count | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 50 m | ≤ 9600 bps | ≤ 5 | Termination not required |
| 50–500 m | 9600–38400 bps | 5–20 | Recommended |
| > 500 m | ≥ 38400 bps | Many nodes | Mandatory |

6. Conclusion
Whether a Modbus RTU network requires termination resistors depends on distance, baud rate, device count, and cable quality.
For short, low-speed, and simple networks, termination is optional.
For long, high-speed, or complex networks, termination is essential to ensure reliable communication.
In practice, engineers should validate with real measurements and apply the principle of suitability rather than rigidly following theory.
