British Standard Pipe Parallel (BSPP) and G threads are commonly used in pipe fittings and are part of the British Standard Pipe (BSP) thread family. Although similar in some respects, these threads serve slightly different purposes and have unique characteristics that make them suited for specific applications. Understanding their differences, how they seal, and where they are commonly used can help ensure compatibility and safety in plumbing, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems.
1. What Are BSPP and G Threads?
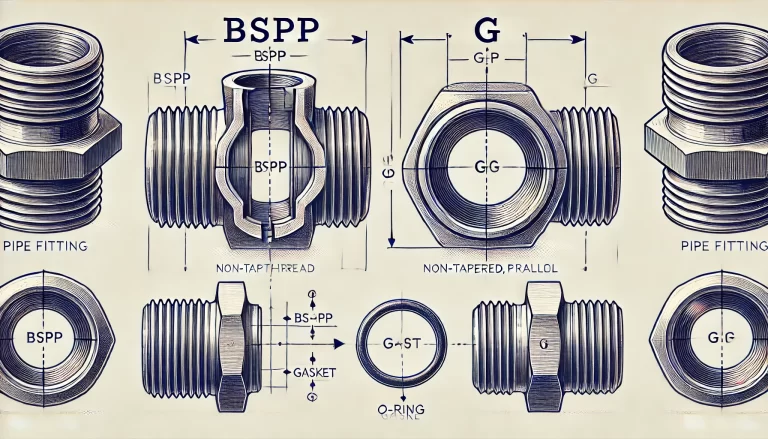
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): BSPP threads are part of the British Standard Pipe thread system, which was developed to standardize pipe sizes and improve compatibility across different types of fittings. The “P” in BSPP indicates that it is a parallel or straight thread. In other words, the diameter of the thread remains constant along its length. BSPP threads are defined by the British Standard 2779 and are used for non-tapered pipe fittings.
G Thread: G threads are also parallel or straight threads and are defined by ISO 228, which is an international standard for pipe threads that do not seal on the threads themselves. In many cases, G threads are considered synonymous with BSPP threads because they share the same dimensional specifications and can often be interchanged. However, G threads are often marked with the letter “G” on fittings to designate compliance with ISO standards, rather than British standards.

2. Key Differences Between BSPP and G Threads
Though BSPP and G threads can be interchangeable in many contexts, they differ in these important aspects:
Standardization: BSPP threads are defined under the British Standard BS 2779, while G threads follow the ISO 228 standard. This difference is mostly in terminology and labeling; both threads are parallel and have similar sizing.
Designation and Labeling: BSPP threads are often marked with “BSPP” or “BSP,” while G threads are labeled with the letter “G” as per ISO standards. This distinction can be crucial in industries where adherence to specific standards is mandatory.
3. How BSPP and G Threads Achieve Sealing
Since both BSPP and G threads are parallel, they do not seal by the threads themselves (unlike tapered threads like BSPT or NPT, which achieve sealing through the interference fit of the taper). Instead, these threads require an additional sealing mechanism to ensure a leak-free connection. There are two main sealing methods for BSPP and G threads:
Face Sealing: A flat sealing surface, such as a metal or elastomeric gasket, is used to create a seal at the end of the fitting. When the fitting is tightened, the gasket compresses and forms a seal against the flat face of the mating part. This type of sealing is common in hydraulic and pneumatic systems where higher pressures may be present.
O-Ring Sealing: Another common method is to use an O-ring that sits at the end of the male fitting. When the fitting is screwed into a matching female port, the O-ring compresses, forming a tight seal. O-ring sealing is often found in applications where consistent, reliable sealing is essential, and it provides an extra layer of protection against leaks.
4. Applications of BSPP and G Threads
Both BSPP and G threads are widely used in applications where reliable connections are needed but thread sealing alone is insufficient. Here are some of the key applications:
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: BSPP and G threads are popular in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, especially in Europe, due to their compatibility with high-pressure applications when used with O-rings or sealing washers. These systems require precise, leak-free connections, making BSPP and G threads with face-sealing or O-ring-sealing highly desirable.
Plumbing and Water Supply: In some water supply systems and plumbing applications, BSPP and G threads are used where a non-tapered thread connection is necessary, particularly when consistent diameter and alignment are important. However, they are often limited to indoor applications or low-pressure systems unless a sealing washer or O-ring is added for extra protection.
Process and Chemical Industries: Due to their ability to form reliable, leak-free connections, BSPP and G threads are frequently used in process industries where chemical handling and processing occur. When paired with the appropriate seals, these threads can handle a variety of media, from corrosive chemicals to high-temperature fluids.
5. Identifying and Choosing Between BSPP and G Threads
To identify BSPP and G threads, you can look for specific markings:
Markings: BSPP fittings are typically labeled with “BSP” or “BSPP,” while G threads are marked with “G.” Since they are parallel threads, you can also measure the diameter of the threads, which should remain consistent along the length of the fitting.
Compatibility and Selection: In general, BSPP and G threads can be used interchangeably, but the selection often depends on the regional standards in place. For instance, Europe tends to use ISO-compliant G threads more frequently, while the UK may prefer BSP standards.
6. Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Due to the similarities between BSPP and G threads, there are some common misconceptions and potential pitfalls:
Assuming They Seal by Themselves: Both BSPP and G threads are parallel and do not seal through thread interference. Always use an additional sealing element, such as an O-ring or gasket, to avoid leaks.
Confusing Tapered Threads with Parallel Threads: BSPP/G threads (parallel) should not be confused with BSPT or NPT threads (tapered). Mixing parallel and tapered threads in a system can lead to cross-threading, leaks, or even system failure.
Conclusion
BSPP and G threads are versatile and effective for creating reliable connections, especially in industries that rely on non-tapered fittings. They are most commonly found in systems where additional sealing elements, such as O-rings or washers, are used to create a tight, leak-proof connection. While BSPP and G threads are often interchangeable, understanding their distinctions, applications, and sealing requirements will help ensure that your system remains safe and functional.
